Volume 23, Number 5—May 2017
Research
Prevention of Chronic Hepatitis B after 3 Decades of Escalating Vaccination Policy, China
Figure 4
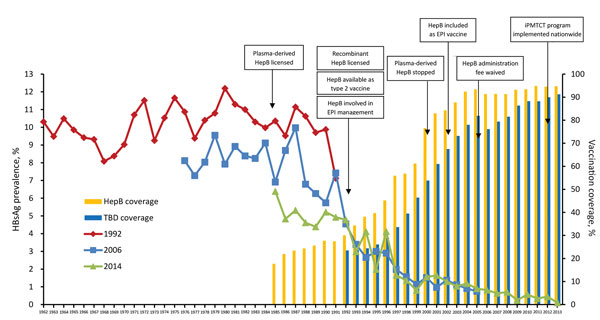
Figure 4. Prevalence of HBsAg and 3-dose HepB coverage for each birth cohort and major vaccination program milestones for hepatitis B virus, China, 1962–2014. HBsAg prevalence is shown in 3 curves, 1 for each national serologic survey (1992, 2006, and 2014). HepB coverage is shown in bars. Type 2 vaccines are private sector vaccines that are not included in the free national EPI system but must be paid for out-of-pocket. HepB coverage was defined as the percentage of children <15 years of age who received 3 doses of HepB before reaching 12 months of age. Coverage levels of children born during 1985–1991, 1992–2005, and 2006–2013 were determined from the 1992, 2006, and 2014 surveys, respectively. TBD coverage was defined as the percentage of newborn infants who received a dose of HepB within 24 hours of birth. The iPMTCT program provides free HBsAg screening of pregnant women and free hepatitis B immunoglobulin for hepatitis B virus–exposed infants. EPI, Expanded Program on Immunization; HBsAg, hepatitis B virus surface antigen; HepB, hepatitis B vaccine; iPMTCT, integrated Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission, TBD, timely birth dose.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.