Volume 23, Number 6—June 2017
Dispatch
Sustainability of High-Level Isolation Capabilities among US Ebola Treatment Centers
Figure 2
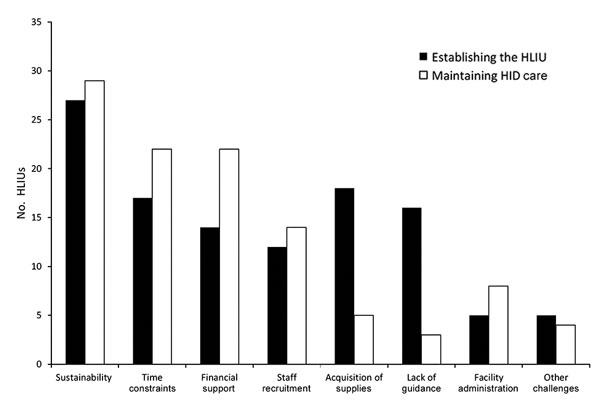
Figure 2. Challenges to establishing an HLIU and to maintaining HID care reported by survey respondents, United States, 2016 (n = 32 HLIUs). Other challenges include external support, lack of dedicated unit space, competing priorities, staffing needs, and decreasing hospital capacities. HLIU, high-level isolation unit; HID, highly infectious disease.
Page created: May 16, 2017
Page updated: May 16, 2017
Page reviewed: May 16, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.