Volume 24, Number 12—December 2018
Research
Human Exposure to Novel Bartonella Species from Contact with Fruit Bats
Figure
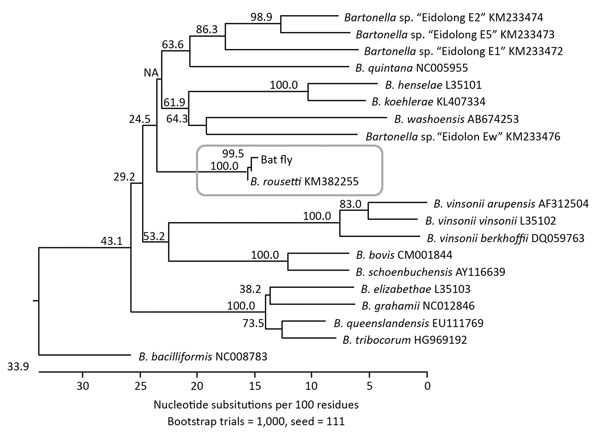
Figure. Phylogenetic relationships of Bartonella rousetti (proposed name) obtained from Egyptian fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus) collected in Nigeria, 2010 and 2013, and other Bartonella species and bat-associated Bartonella based on internal transcribed spacer sequences. The neighbor-joining method by the Kimura 2-parameter distance method and bootstrap calculation was conducted with 1,000 replicates for phylogenetic analysis. The internal transcribed spacer sequence obtained from the bat flies was closely clustered with B. rousetti. GenBank accession numbers are provided for the B. rousetti sequence and the comparison sequences.
1Team members are listed at the end of this article.
Page created: November 20, 2018
Page updated: November 20, 2018
Page reviewed: November 20, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.