Volume 24, Number 6—June 2018
Research Letter
Reassortant Clade 2.3.4.4 of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N6) Virus, Taiwan, 2017
Figure
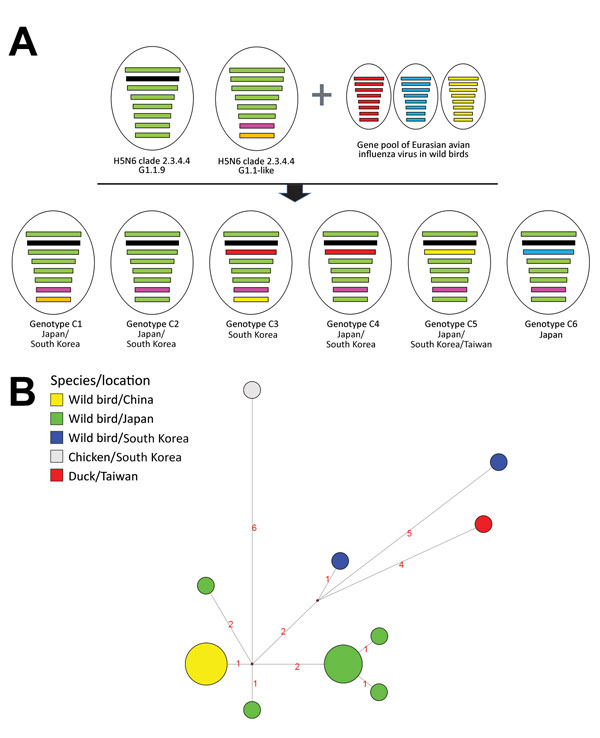
Figure. Genome constellation of influenza A(H5N6) viruses identified in East Asia during 2016–2017 and median-joining phylogenetic network of genotype C5. A) Viruses are represented by ovals containing horizontal bars that represent 8 gene segments (top to bottom: polymerase basic 2, polymerase basic 1, polymerase acidic, hemagglutinin, nucleoprotein, neuraminidase, matrix, and nonstructural). The colors of gene segments denote the genetic origins as previously described by Takemae et al. (7): green and black, G1.1.9 genotypes from China; pink and orange, G1.1-like genotypes from China; other colors, avian influenza lineages from Eurasia. B) Median-joining phylogenetic network of genotype C5 was constructed from the hemagglutinin gene and includes all the most parsimonious trees linking the sequences. Each unique sequence is represented by a circle sized relative to its frequency in the dataset. Branch length is proportional to the number of mutations. Isolates are colored according to the origin of the sample.
References
- Lee DH, Bertran K, Kwon JH, Swayne DE. Evolution, global spread, and pathogenicity of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5Nx clade 2.3.4.4. J Vet Sci. 2017;18(S1):269–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhao G, Gu X, Lu X, Pan J, Duan Z, Zhao K, et al. Novel reassortant highly pathogenic H5N2 avian influenza viruses in poultry in China. PLoS One. 2012;7:e46183. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee DH, Bahl J, Torchetti MK, Killian ML, Ip HS, DeLiberto TJ, et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses and generation of novel reassortants, United States, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:1283–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sims L, Harder T, Brown I, Gaidet N, Belot G. Dobschuetz Sv, et al. Highly pathogenic H5 avian influenza in 2016 and 2017—observations and future perspectives [cited 2017 Dec 15]. http://agritrop.cirad.fr/585953
- Global Consortium for H5N8 and Related Influenza Viruses. Role for migratory wild birds in the global spread of avian influenza H5N8. Science. 2016;354:213–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Okamatsu M, Ozawa M, Soda K, Takakuwa H, Haga A, Hiono T, et al. Characterization of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A(H5N6), Japan, November 2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:691–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Takemae N, Tsunekuni R, Sharshov K, Tanikawa T, Uchida Y, Ito H, et al. Five distinct reassortants of H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza A viruses affected Japan during the winter of 2016-2017. Virology. 2017;512:8–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee EK, Song BM, Lee YN, Heo GB, Bae YC, Joh SJ, et al. Multiple novel H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses, South Korea, 2016. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;51:21–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee MS, Chen LH, Chen YP, Liu YP, Li WC, Lin YL, et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses H5N2, H5N3, and H5N8 in Taiwan in 2015. Vet Microbiol. 2016;187:50–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:1312–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.