Avian Influenza A(H9N2) Virus in Poultry Worker, Pakistan, 2015
Muzaffar Ali, Tahir Yaqub, Nadia Mukhtar, Muhammad Imran, Aamir Ghafoor, Muhammad Furqan Shahid, Muhammad Naeem, Munir Iqbal, Gavin J.D. Smith

, and Yvonne C.F. Su
Author affiliations: University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan (M. Ali, T. Yaqub, M. Imran, A. Ghafoor, M.F. Shahid); Health Care Department, Government of Punjab, Lahore (N. Mukhtar); Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan (M. Naeem); The Pirbright Institute, Compton Laboratory, Newbury, UK (M. Iqbal); Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, USA (G.J.D. Smith); Duke-National University Singapore Medical School, Singapore (G.J.D. Smith, Y.C.F. Su)
Main Article
Figure
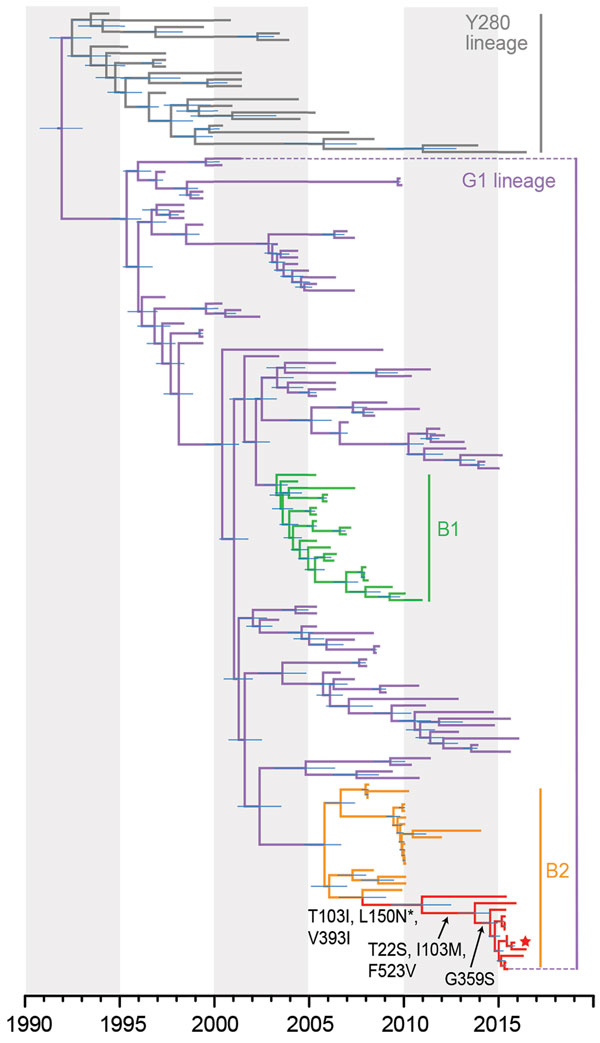
Figure. Evolutionary relationships of the influenza A virus H9-HA gene isolated from avian and human hosts, Pakistan, 1998–2016. The phylogeny was generated using the uncorrelated lognormal relaxed molecular clock, the SRD06 codon position model, HKY85 plus gamma substitution model, and a Gaussian Markov random field (GMRF) Bayesian skyride in BEAST version 1.8.4. Two independent runs of 100 million Markov chain Monte Carlo generations were performed. Horizontal node bars represent the 95% highest posterior density intervals. Red branches indicate new sequences generated from this study, and the new human isolate is marked by a red star. Black arrows indicate the amino acid mutations (H9 numbering) for the 2015–2016 Pakistan lineage, and asterisk indicates site under positive selection.
Main Article
Page created: December 18, 2018
Page updated: December 18, 2018
Page reviewed: December 18, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
