Volume 25, Number 10—October 2019
Synopsis
Localized Outbreaks of Epidemic Polyarthritis among Military Personnel Caused by Different Sublineages of Ross River Virus, Northeastern Australia, 2016–2017
Figure 3
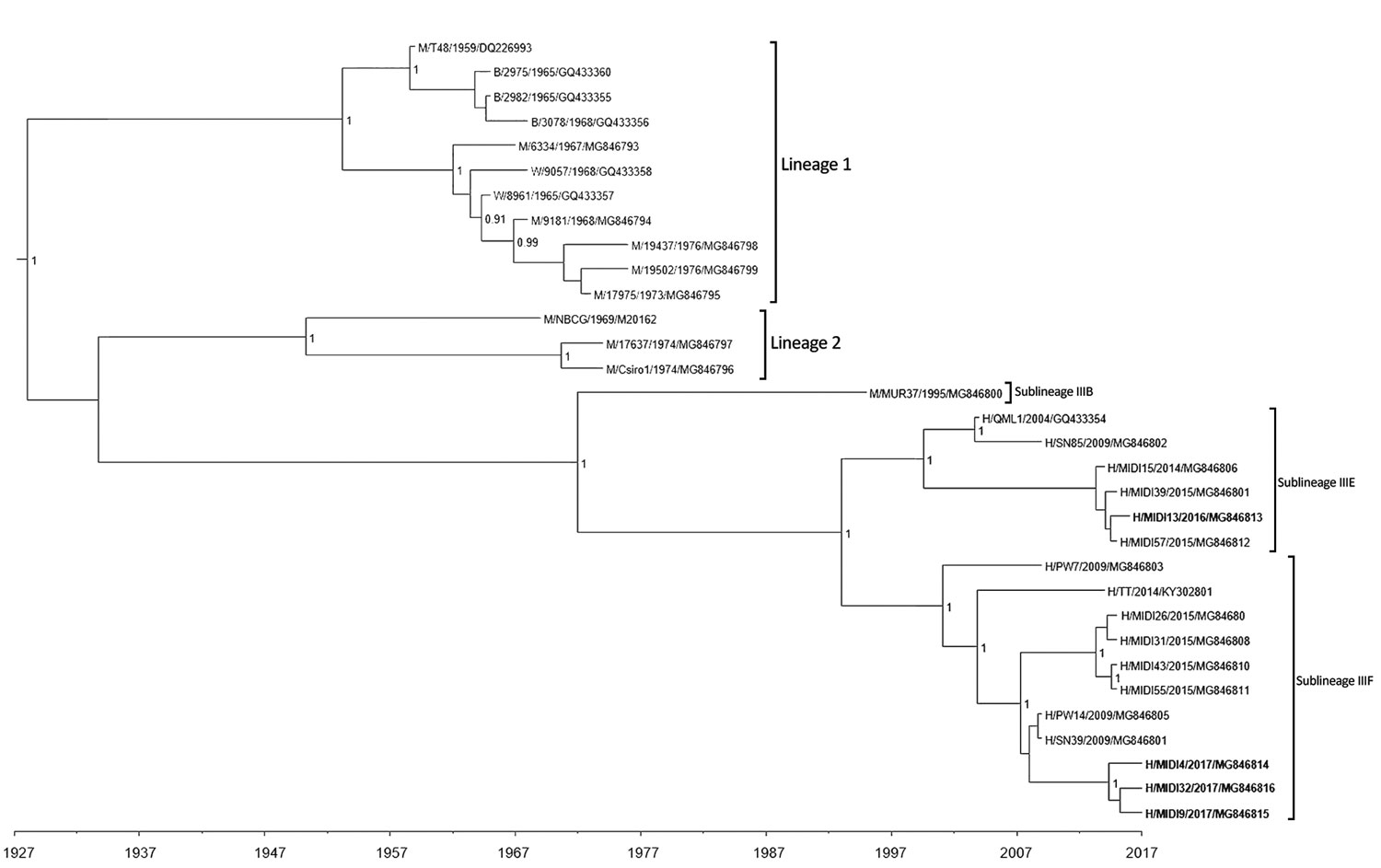
Figure 3. Maximum clade credibility tree based on analysis of 32 complete Ross River virus nsP3 sequences (1,650 nt) from outbreaks among Australian Defence Force personnel during and after training in Shoalwater Bay Training Area, northeastern Australia, 2016–2017. Isolates were classified into 2 distinct sublineages in lineage III. We used Bayesian phylogenetic analysis method in BEAST software (http://beast.community) to analyze the aligned nsP3 sequences, applying the TN93 plus gamma substitution model with a strict clock model, a chain length of 10 million, and a 10% burn-in using TreeAnnotator (https://beast.community/treeannotator). Numbers at nodes indicate the posterior probability values >0.8. The naming convention of the strains was name of host/strain/year of isolation/GenBank accession number. B, birds; H, humans; M, mosquitoes; W, wallabies.