Volume 25, Number 5—May 2019
Dispatch
Severe Myasthenic Manifestation of Leptospirosis Associated with New Sequence Type of Leptospira interrogans
Figure 2
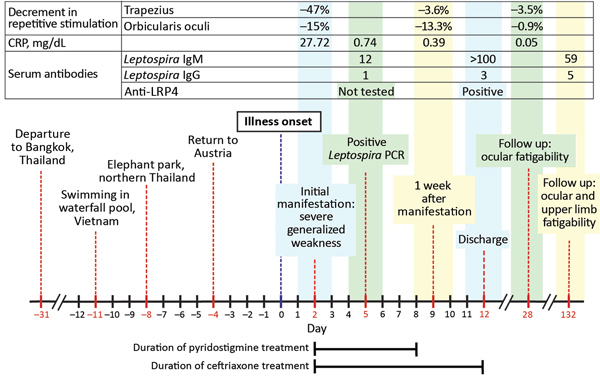
Figure 2. Timeline of medical history for patient with severe myasthenic manifestation of leptospirosis, including results of relevant neurologic and laboratory investigations. Decrement in repetitive stimulation denotes the maximum decrease in amplitude of the fourth or fifth compound muscle action potential waveform during supramaximal repetitive nerve stimulation at 3 Hz. A decrement >10% is regarded as pathologic (6). Leptospira ELISA cutoff values: IgG, <10 U/mL negative, 15 U/mL positive; IgM, <15 U/mL negative, >20 U/mL positive. CRP, C-reactive protein; LRP4, lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4.
References
- Bharucha NE. Infections of the nervous system. In: Bradley’s neurology in clinical practice. Bradley DR, Fenichel GM, editors. Butterworth Heinemann: Boston; 1991. p. 1074–5.
- Panicker JN, Mammachan R, Jayakumar RV. Primary neuroleptospirosis. Postgrad Med J. 2001;77:589–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boonsilp S, Thaipadungpanit J, Amornchai P, Wuthiekanun V, Bailey MS, Holden MT, et al. A single multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme for seven pathogenic Leptospira species. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e1954. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- AAEM Quality Assurance Committee. American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Literature review of the usefulness of repetitive nerve stimulation and single fiber EMG in the electrodiagnostic evaluation of patients with suspected myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2001;24:1239–47. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vincent A, Huda S, Cao M, Cetin H, Koneczny I, Rodriguez-Cruz P, et al. Serological and experimental studies in different forms of myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1413:143–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yan M, Xing GL, Xiong WC, Mei L. Agrin and LRP4 antibodies as new biomarkers of myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1413:126–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zisimopoulou P, Evangelakou P, Tzartos J, Lazaridis K, Zouvelou V, Mantegazza R, et al. A comprehensive analysis of the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of anti-LRP4 in myasthenia gravis. J Autoimmun. 2014;52:139–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodríguez Cruz PM, Al-Hajjar M, Huda S, Jacobson L, Woodhall M, Jayawant S, et al. Clinical features and diagnostic usefulness of antibodies to clustered acetylcholine receptors in the diagnosis of seronegative myasthenia gravis. JAMA Neurol. 2015;72:642–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Leis AA, Szatmary G, Ross MA, Stokic DS. West nile virus infection and myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 2014;49:26–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Molko N, Simon O, Guyon D, Biron A, Dupont-Rouzeyrol M, Gourinat AC. Zika virus infection and myasthenia gravis: report of 2 cases. Neurology. 2017;88:1097–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ramos-Fransi A, Rojas-García R, Segovia S, Márquez-Infante C, Pardo J, Coll-Cantí J, et al.; Myasthenia NMD-ES Study Group. Myasthenia gravis: descriptive analysis of life-threatening events in a recent nationwide registry. Eur J Neurol. 2015;22:1056–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pradhan S, Tandon R, Kishore J. Combined involvement of muscle, nerve, and myoneural junction following leptospira infection. Neurol India. 2012;60:514–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Makhija P, Gopinath S, Kannoth S, Radhakrishnan K. A case of post-leptospirosis autoimmune epilepsy presenting with sleep-related hypermotor seizures. Epileptic Disord. 2017;19:456–60.PubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: April 18, 2019
Page updated: April 18, 2019
Page reviewed: April 18, 2019
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.