Volume 25, Number 7—July 2019
Research
Essential Role of Interferon Response in Containing Human Pathogenic Bourbon Virus
Figure 5
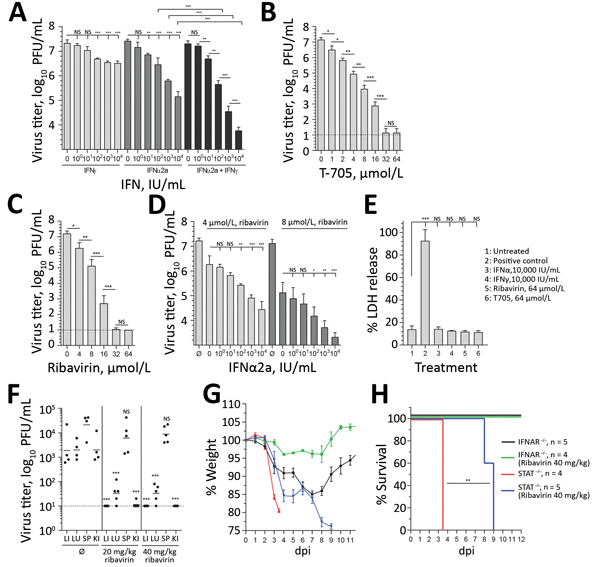
Figure 5. Antiviral treatment against BRBV. A–D) Huh7 cells infected with BRBV (multiplicity of infection 0.001) had viral titers determined at 48 hpi. Shown are the arithmetic means (+SD) of log-transformed values of 3 independent experiments. The cells were treated with increasing amounts of IFN-α2a, IFN-γ, or equal amounts of both IFNs 16 h prior and 2 hpi (A); increasing amounts of the antiviral drugs favipiravir (T705) and ribavirin 2 hpi (B, C); or a combination of ribavirin and IFN-α2a (D). E) To evaluate the cytotoxicity of these compounds, cells were treated with the indicated concentrations for 48 h, or as a positive control the cells were treated with lysis buffer. LDH activity in the supernatant was determined (normalized to positive control [n = 3, mean +SD]). Statistical analyses were performed with a 1-way analysis of variance (Tukey multiple comparison test). F) IFNAR−/− animals (n = 5) treated by intraperitoneal injection with 0.9% NaCl (mock-treated) or 20 or 40 mg/kg/d ribavirin starting 4 hpi with 1,000 PFU of BRBV. At 4 dpi, viral titers were determined in liver, lung, spleen, and kidney. G, H) IFNAR−/− or STAT1−/− mice treated until day 7 dpi with ribavirin (40 mg/kg/d) as in panel F. Weight (mean +SEM) and survival were monitored daily. The animals were euthanized if they lost >25% bodyweight or showed signs of severe illness. H) Statistical analysis for the survival curve performed with a log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. BRBV, Bourbon virus; dpi, days postinfection; IFN, interferon; IFNAR, type I interferon receptor; hpi, hours postinfection; KI, kidney; LI, liver; LU, lung; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; NS, nonsignificant; SP, spleen; ∅, mock-treated (control). ***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05.