Volume 25, Number 7—July 2019
Dispatch
Whole-Blood Testing for Diagnosis of Acute Zika Virus Infections in Routine Diagnostic Setting
Figure
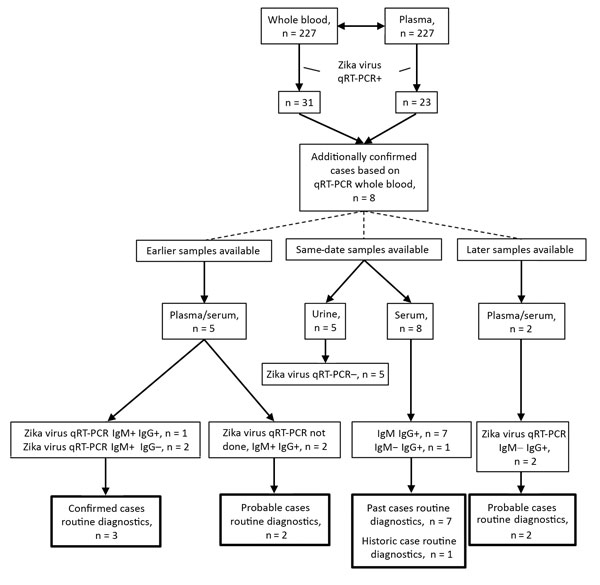
Figure. Overview of results of Zika virus diagnostic testing on total sample sets for 8 Zika patients additionally confirmed with Zika virus infection on the basis of whole-blood qRT-PCR. IgG, Zika virus IgG ELISA; IgM, Zika virus IgM ELISA; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription PCR; +, positive; –, negative.
1Current affiliation: Microvida, Roosendaal, the Netherlands.
2Current co-affiliation: Netherlands Centre for Infectious Disease Control, National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, Bilthoven, the Netherlands.
Page created: June 17, 2019
Page updated: June 17, 2019
Page reviewed: June 17, 2019
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.