Volume 25, Number 8—August 2019
Dispatch
Emergent Invasive Group A Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, United States, 2015–2018
Figure 2
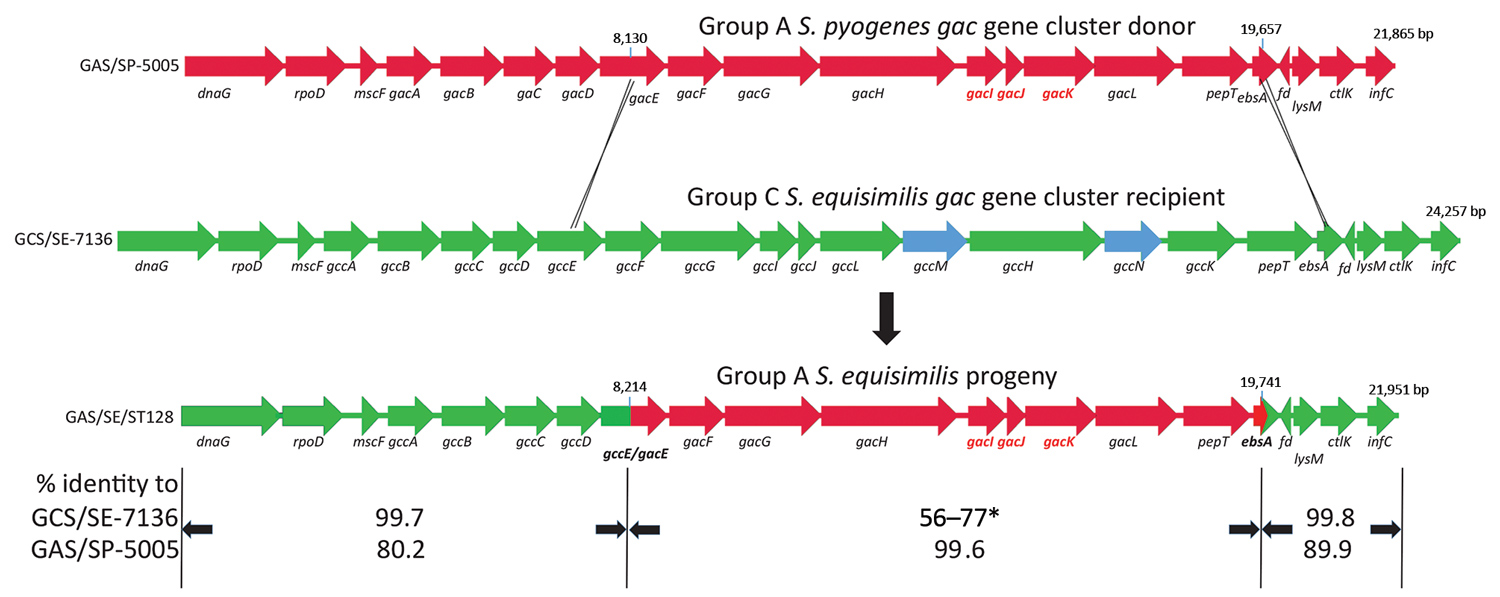
Figure 2. Ancestral recombination event depicting Streptococcus pyogenes group A carbohydrate gene donor (GAS/SP-5005; GenBank accession no. NC007297), group C S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis recipient (GCS/SE7136; GenBank accession no. NCTC7136), and progeny group A S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis progeny (GAS/SE/ST128) described in study of emergent invasive group A Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis, United States, 2015–2018. The deduced crossover points between the group A gene cluster (red) donor and group C (green) recipient strains are shown. The 3 genes required for inclusion of the immunodominant N-acetylglucosamine side chain within the group A carbohydrate (gacI, gacJ, and gacK) are shown in red. The coordinates of the fragment transferred that is highly conserved between the donor and the progeny are indicated. The length of the 3 genomic regions are indicated. The gacE/gccE and ebsA genes are shown as green/red hybrids. The extra gcc cluster genes not conserved within the gac cluster are shown in blue. The relative sequence identities of the 3 different regions of progeny (bottom) gac cluster genes with the group A S. pyogenes donor (top) and group C S. equisimilis recipient (middle) are indicated. The middle segment (asterisk) indicates a range of 56%–77% sequence identity between each of the 8 structural genes (gacF–pepT) that were received intact from the S. pyogenes donor. The gac cluster genes are described in more detail in van Sorge et al. (1). Gene assignments are as follows: dnaG, DNA primase; rpoD, major RNA polymerase sigma factor; mscF, metal sulfur complex assembly factor; gacA-L, group A carbohydrate biosynthetic genes (putative functions described in van Sorge et al. [1]); gccA-N, group C carbohydrate biosynthetic genes. gccA-L are functional homologs of gacA-L. gccM and gccN putatively encode an additional glycosyl transferase and UDP-monosaccharide 4-epimerase, respectively; ebsA, pore-forming protein; fd, ferredoxin (complement strand); ctlK, cytidylate kinase; infC, translation initiation factor IF-3.
References
- van Sorge NM, Cole JN, Kuipers K, Henningham A, Aziz RK, Kasirer-Friede A, et al. The classical lancefield antigen of group a Streptococcus is a virulence determinant with implications for vaccine design. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:729–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chochua S, Metcalf BJ, Li Z, Rivers J, Mathis S, Jackson D, et al. Population and whole genome sequence based characterization of invasive group A streptococci recovered in the United States during 2015. MBio. 2017;8:e01422–17. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brandt CM, Haase G, Schnitzler N, Zbinden R, Lütticken R. Characterization of blood culture isolates of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis possessing Lancefield’s group A antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:4194–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tanaka D, Isobe J, Watahiki M, Nagai Y, Katsukawa C, Kawahara R, et al.; Working Group for Group A Streptococci in Japan. Genetic features of clinical isolates of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis possessing Lancefield’s group A antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:1526–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ahmad Y, Gertz RE Jr, Li Z, Sakota V, Broyles LN, Van Beneden C, et al. Genetic relationships deduced from emm and multilocus sequence typing of invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis and S. canis recovered from isolates collected in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2046–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McMillan DJ, Bessen DE, Pinho M, Ford C, Hall GS, Melo-Cristino J, et al. Population genetics of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis reveals widely dispersed clones and extensive recombination. PLoS One. 2010;5:
e11741 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Lancefield RC. The antigenic complex of Streptococcus haemolyticus: I. Demonstration of a type-specific substance in extracts of Streptococcus haemolyticus. J Exp Med. 1928;47:91–103. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Walker MJ, Brouwer S, Forde BM, Worthing KA, McIntyre L, Sundac L, et al. Detection of epidemic scarlet fever group A Streptococcus in Australia. Clin Infect Dis. 2019; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Coligan JE, Kindt TJ, Krause RM. Structure of the streptococcal groups A, A-variant and C carbohydrates. Immunochemistry. 1978;15:755–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Enright MC, Spratt BG, Kalia A, Cross JH, Bessen DE. Multilocus sequence typing of Streptococcus pyogenes and the relationships between emm type and clone. Infect Immun. 2001;69:2416–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Broyles LN, Van Beneden C, Beall B, Facklam R, Shewmaker PL, Malpiedi P, et al. Population-based study of invasive disease due to beta-hemolytic streptococci of groups other than A and B. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:706–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar