Volume 26, Number 1—January 2020
Research
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus Hemorrhagic Disease in Asian Elephant Calves in Logging Camps, Myanmar
Figure 3
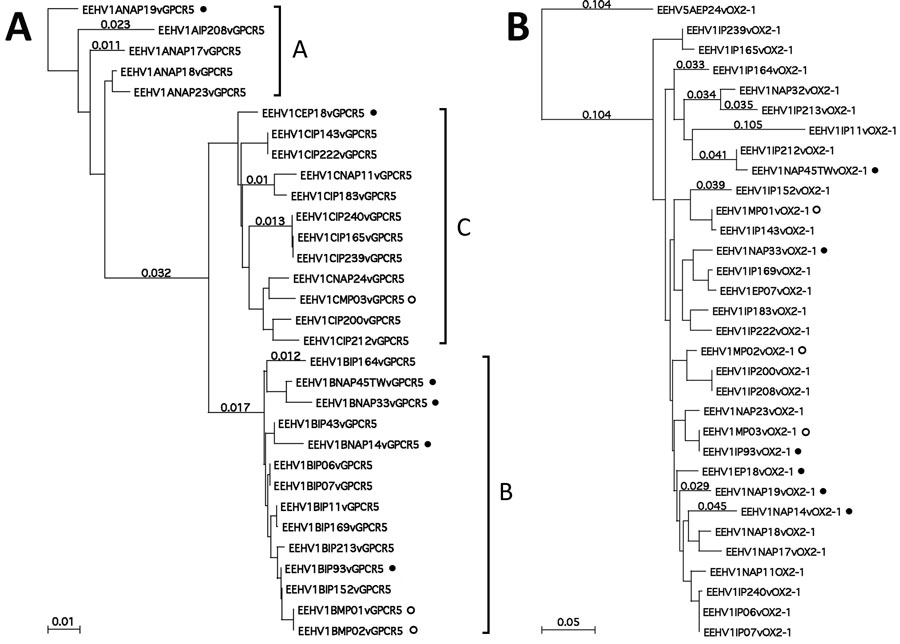
Figure 3. Protein level phylogenetic trees for Asian elephant calves that had endotheliotropic herpesvirus hemorrhagic disease in logging camp, Myanmar. Shown are comparison of examples of Asian EEHV1 at 2 representative hypervariable loci. A) EEHV1 E5(vGPCR5). B) E54(vOX2-1). Bayesian linear phylogenetic trees were generated from translated amino acid data in MEGA5.4.6 (https://www.megasoftware.net) by using similar aligned datasets as in Figure 2. Evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum-likelihood method based on the Jones–Taylor–Thornton matrix-based model with the bootstrap consensus tree. Analysis in panel A involved 31 nt sequences with 303 aa positions in the final dataset with EEHV1B(NAP19) as outgroup. Analysis in panel B involved 32 nt sequences with 244 aa positions in the final dataset and with EEHV5A(EP24) as outgroup. Numbers along branches are bootstrap values. Some representative branch length values are provided. The 3 major subtype clusters are indicated as A, B, or C for E5(vGPCR5) along the right side of panel A, but no similar dramatic subtype clustering was discernable for E54(vOX2-1). All 6 examples in which the genomes have classic EEHV1B type core chimeric domain (CDI, CDII, and CDIII) features elsewhere are indicated by solid circles. Positions of the 3 cases from Myanmar are indicated by open circles. Scale bars indicate amino acid substitutions per site. EEHV, elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus.