Volume 26, Number 10—October 2020
Dispatch
Human Adenovirus B7d–Associated Urethritis after Suspected Sexual Transmission, Japan
Figure 2
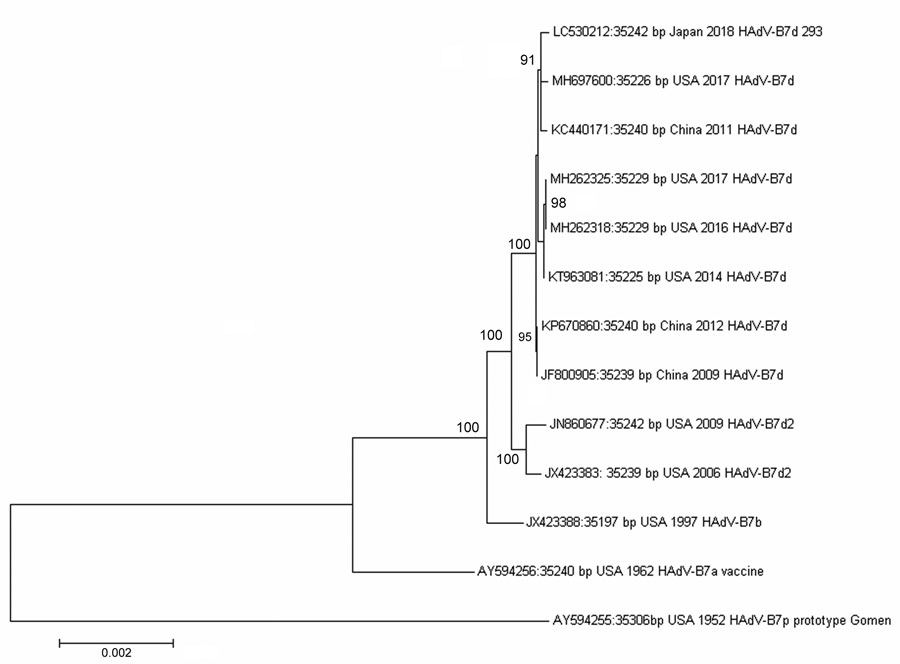
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of human adenovirus genome type 7 whole-genome sequencing in study of human adenovirus B7d–associated urethritis, Japan. We isolated 293 strain and compared it with other human adenovirus type 7 reference strains. We aligned genomic sequences using ClustalW (http://www.clustal.org) and constructed the neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree using MEGA version 7.0 software (https://megasoftware.net). Numbers at selected nodes indicate level of support using 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Scale bar indicates the estimated number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Sequence names are derived from the GenBank accession number, geographic location, and year of sample collection and virus type.
Page created: September 07, 2020
Page updated: September 17, 2020
Page reviewed: September 17, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.