Volume 26, Number 11—November 2020
Dispatch
SARS-CoV-2 Virus Culture and Subgenomic RNA for Respiratory Specimens from Patients with Mild Coronavirus Disease
Figure 2
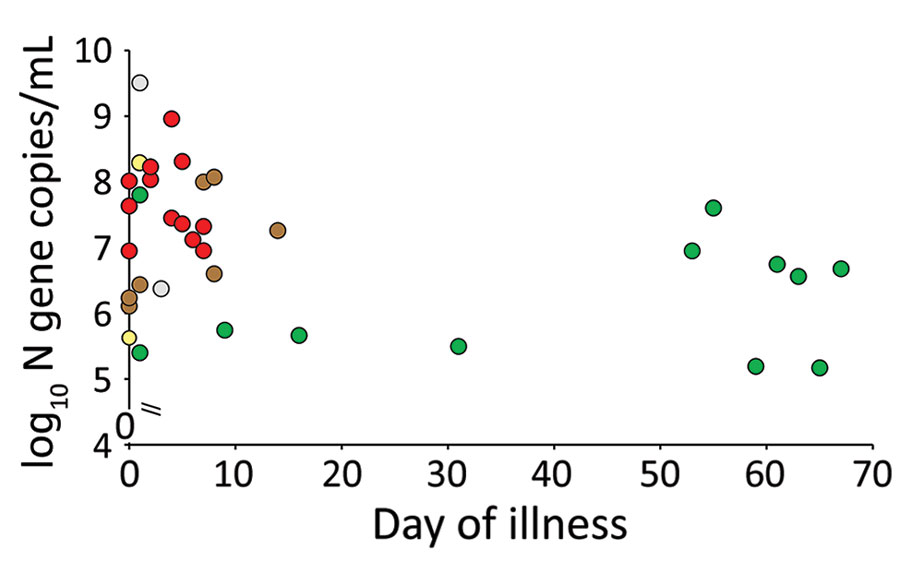
Figure 2. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 viral RNA load, virus culture, and subgenomic virus RNA (sgRNA) in relation to days after onset of illness for patients with mild coronavirus disease, Hong Kong. Red indicates culture and sgRNA positive, green indicates culture and sgRNA negative, yellow indicates culture positive and sgRNA negative, brown indicates culture negative and sgRNA positive, and gray indicates culture positive and no sgRNA data (because of insufficient specimen).
Page created: July 28, 2020
Page updated: October 19, 2020
Page reviewed: October 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.