Volume 26, Number 11—November 2020
Letter
COVID-19 Outbreak Associated with Air Conditioning in Restaurant, Guangzhou, China, 2020
Figure 2
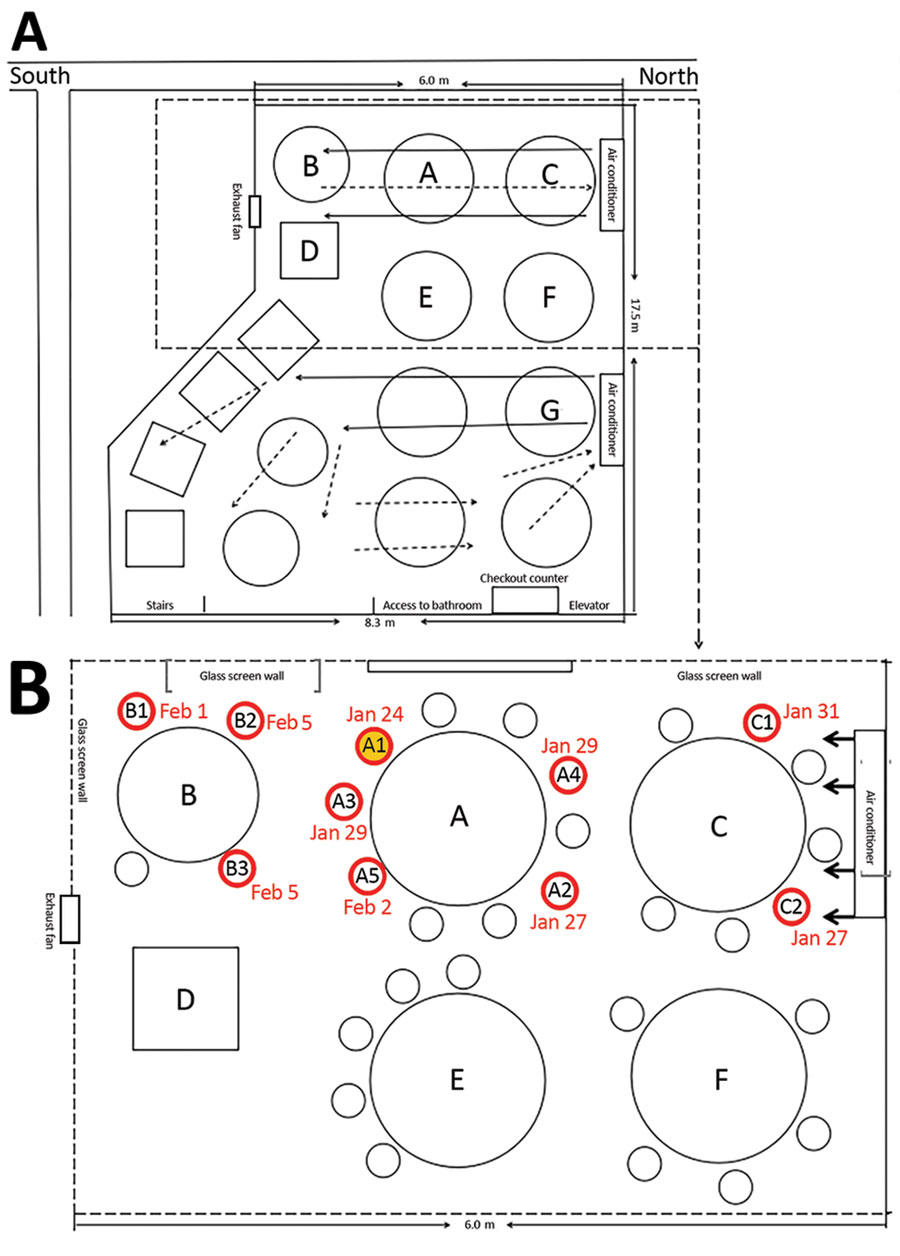
Figure 2. Air flow (A) and seating diagram (B) for restaurant described in study of COVID-19 outbreak associated with air conditioning in restaurant, Guangzhou, China, 2020 (2).
References
- Rule AM. COVID-19 outbreak associated with air conditioning in restaurant, Guangzhou, China, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:xxx.
- Lu J, Gu J, Li K, Xu C, Su W, Lai Z, et al. COVID-19 outbreak associated with air conditioning in restaurant, Guangzhou, China, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:1628–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fernstrom A, Goldblatt M. Aerobiology and its role in the transmission of infectious diseases. J Pathogens. 2013;2013:
493960 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P, Joynt GM, et al. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1986–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kim SH, Chang SY, Sung M, Park JH, Bin Kim H, Lee H, et al. Extensive viable Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus contamination in air and surrounding environment in MERS isolation wards. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:363–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tong ZD, Tang A, Li KF, Li P, Wang HL, Yi JP, et al. Potential presymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Zhejiang Province, China, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:1052–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: September 08, 2020
Page updated: October 19, 2020
Page reviewed: October 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.