Volume 26, Number 12—December 2020
Research Letter
Autochthonous Ratborne Seoul Virus Infection in Woman with Acute Kidney Injury
Figure
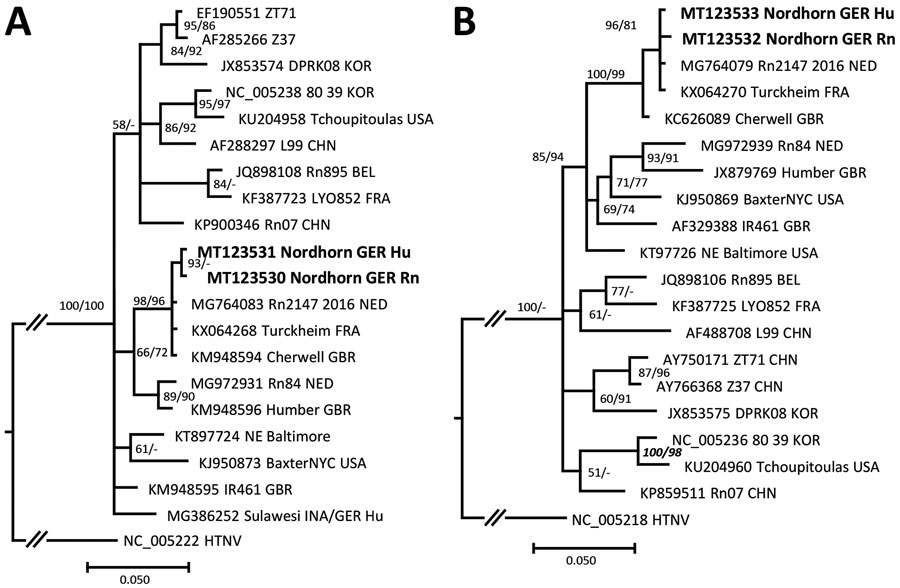
Figure. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the amplified large (L) and small (S) segment regions of human and rat origin from Nordhorn/Germany (strains Nordhorn GER Hu and Nordhorn GER Rn, designated in bold). The consensus tree is based on a 412-nt region of the L segment (A) and a 673-nt region of the S segment (B). Alignments were constructed with Bioedit software package version7.2.5) (https://bioedit.software.informer.com) using the Clustal W Multiple Alignment algorithm. The best fitting substitution model was determined with jModeltest version 2.1.10 (https://github.com/ddarriba/jmodeltest2). Trees were reconstructed with MrBayes version 3.2.6 (http://www.mrbayes.net) and FasttreeMP version 2.1.10 (http://microbesonline.org/fasttree) executed on the CIPRES portal (https://www.phylo.org) according to maximum-likelihood and Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms. The consensus tree is based on Bayesian analyses with 2 × 106 generations, a burn-in phase of 25%, and the Hasegawa-Kishono-Yano substitution model with gamma distribution. Bootstrap values were transferred to the Bayesian tree behind posterior probabilities only if they were >50% and if branches of both trees were consistent. Hantaan virus was used as outgroup. The L and S segment sequences were deposited in GenBank under accession nos. MT123530–33. At the end of the strain names the country of origin is given: BEL, Belgium; CHN, China; FRA, France; GBR, Great Britain; GER, Germany; INA, Indonesia; KOR, South Korea; NED, the Netherlands; USA, United States. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: Robert Koch Institute, Berlin, Germany.