West Nile Virus in Farmed Crocodiles, Zambia, 2019
Edgar Simulundu

, Kunda Ndashe, Herman M. Chambaro, David Squarre, Paul Michael Reilly, Simbarashe Chitanga, Katendi Changula, Andrew N. Mukubesa, Joseph Ndebe, John Tembo, Nathan Kapata, Matthew Bates, Yona Sinkala, Bernard M. Hang’ombe, King S. Nalubamba, Masahiro Kajihara, Michihito Sasaki, Yasuko Orba, Ayato Takada, and Hirofumi Sawa
Author affiliations: Author affiliations: The University of Zambia, Lusaka, Zambia (E. Simulundu, S. Chitanga, K. Changula, A.N. Mukubesa, J. Ndebe, B.M. Hang’ombe, K.S. Nalubamba, A. Takada, H. Sawa); Lusaka Apex Medical University, Lusaka (K. Ndashe); Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan (H.M. Chambaro, D. Squarre, M. Kajihara, M. Sasaki, Y. Orba, A. Takada, H. Sawa); Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock, Lusaka (H.M. Chambaro, Y. Sinkala); Department of National Parks and Wildlife, Chilanga, Zambia (D. Squarre); The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK (D. Squarre); University of Florida, Florida, USA (P.M. Reilly); HerpeZ, University Teaching Hospital, Lusaka (J. Tembo, M. Bates); Zambia National Public Health Institute, Ministry of Health, Lusaka (N. Kapata); University of Zambia–University College London Medical School, Research and Training Programme, Lusaka (N. Kapata); University of Lincoln, Lincoln, UK (M. Bates); University College London, London, UK (M. Bates)
Main Article
Figure
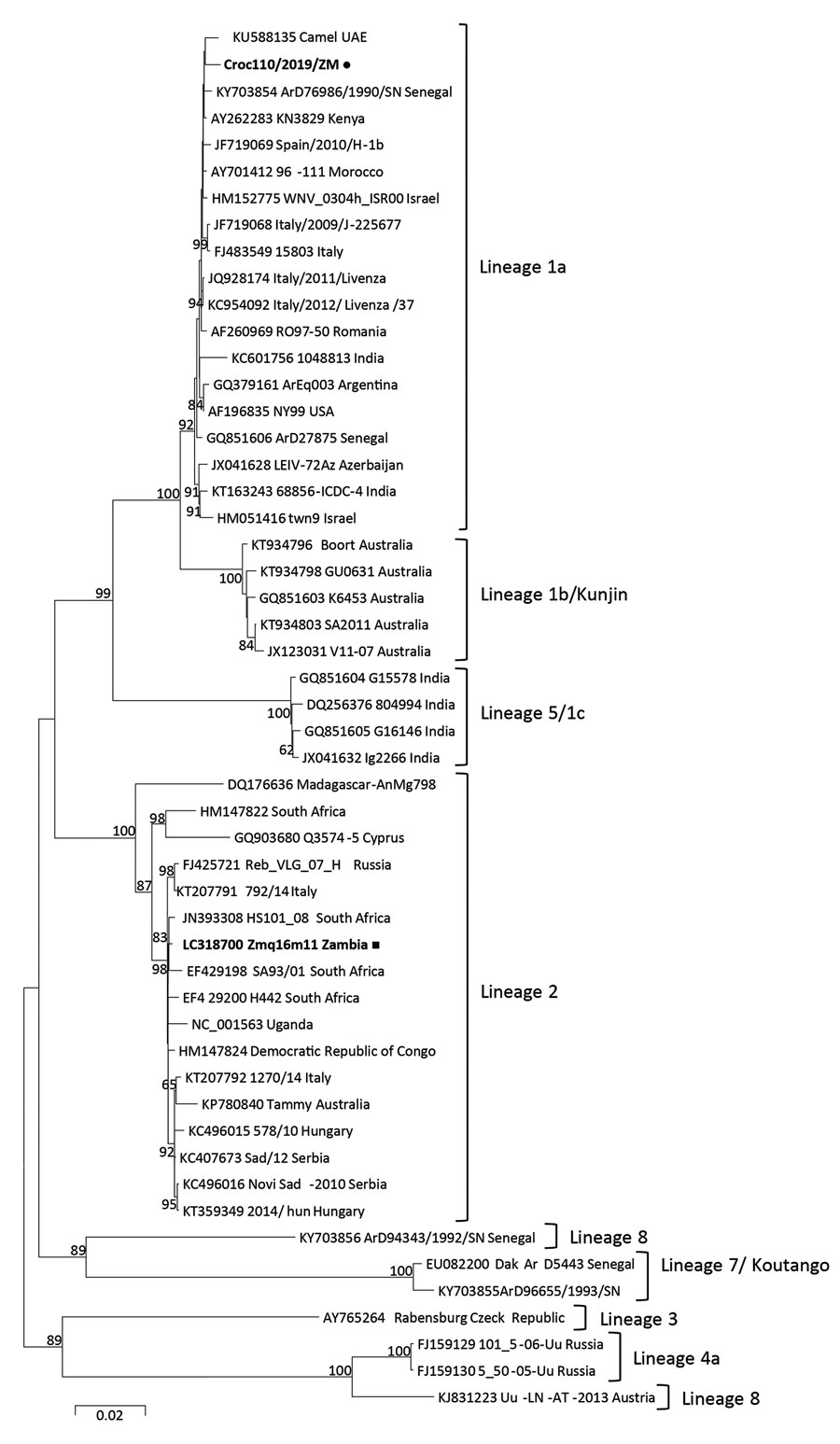
Figure. Phylogenetic tree of complete polyprotein amino acid sequences of West Nile virus (WNV) from farmed crocodiles, Zambia (black dot), and reference sequences. Phylogenetic analysis was conducted by using the maximum likelihood method based on the JTT matrix-based model with 1,000 bootstrap replicates using MEGA6 software (https://www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values >60% are shown next to the branches. The analysis involved 52 amino acid sequences; there were a total of 3,415 positions in the final dataset. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. Reference sequences included in the analysis are shown with their GenBank accession numbers, strain name or source, and country of origin. Black square indicates WNV previously detected from mosquito in the Western Province of Zambia. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Main Article
Page created: March 17, 2020
Page updated: March 17, 2020
Page reviewed: March 17, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
