Volume 26, Number 5—May 2020
Dispatch
Candidatus Rickettsia xinyangensis as Cause of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiosis, Xinyang, China, 2015
Figure
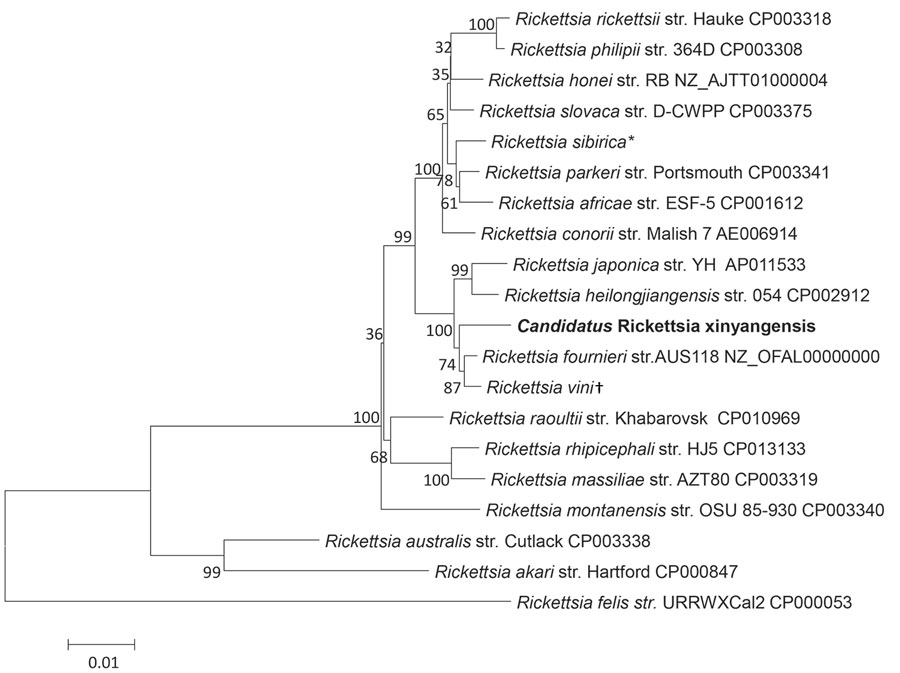
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of concatenated nucleotide sequence of novel spotted fever group Rickettsia, Candidatus R. xinyangensis (bold), Xinyang, China, 2015. The partial nucleotide sequences of genes htrA (421 bp), gltA (1,092 bp), ompA (332 bp), ompB (456 bp), and sca4 (245 bp) were concatenated and compared via the maximum-likelihood method by using the best substitution model found (i.e., Tamura 3-parameter plus gamma) and MEGA version 5.0 (http://www.megasoftware.net). A bootstrap analysis of 1,000 replicates was applied to assess the reliability of the reconstructed phylogenies, and bootstrap values are indicated at branch nodes. Scale bar indicates the number of substitutions per nucleotide position. Str., strain. *Sequence includes the htrA gene from R. sibirica str. 246 (GenBank accession no. AABW01000001) and gltA (accession no. HM050296), ompA (accession no. HM050272), ompB (accession no. HM050273), and sca4 (accession no. HM050295) genes from str. RH05. †Sequence includes the htrA (accession no. KT187396), gltA (accession no. KT187394), and ompA (accession no. KT326194) genes from R. vini str. Breclav; ompB from str. 4GA09_32 (accession no. JF758826); and sca4 from str. IA-CR (accession no. KX159443).
1These first authors contributed equally to this work.