Volume 26, Number 5—May 2020
Research Letter
Serologic Detection of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Functional Antibodies
Figure
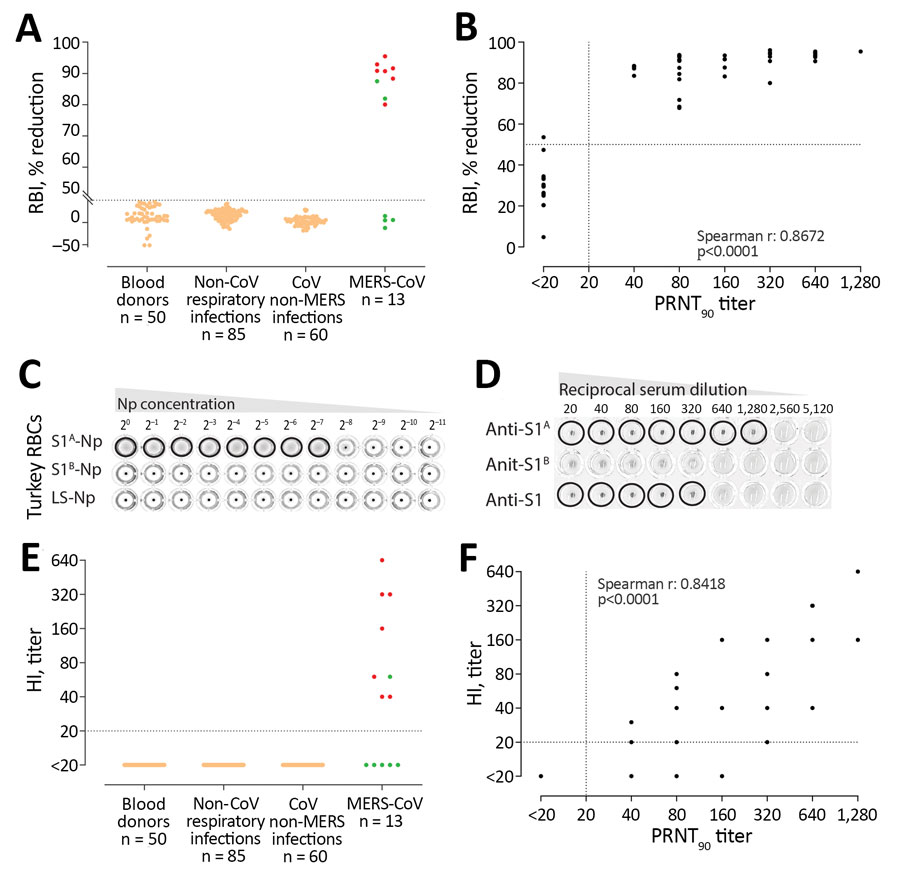
Figure. MERS-CoV–specific RBI and HI assays for MERS-CoV human diagnostics. A) Validation of the specificity of the RBI assay for the detection of MERS-CoV–specific antibodies in humans. Red dots indicate severe illness. Green dots indicate mild illness. B) Correlation between neutralizing and RBI antibody responses after MERS-CoV infection. C) Hemagglutination of turkey erythrocytes using S1A-nanoparticles. S1A-, S1B-, or empty self-assembling lumazine synthase nanoparticles were serially diluted and tested for the ablity to agglutinate turkey RBCs. D) Specificity of the HI assay for the detection of MERS-CoV S1A–directed antibodies. Rabbit anti-S1A, anti S1B, or anti-S1 serum samples were serially diluted and tested for the ability to block S1A-nanoparticles–induced hemagglutination of turkey RBCs. E) Validation of HI assay for the detection of MERS-CoV–specific antibodies in humans. F) Scatter plot correlating PRNT90 neutralization titers and HI titers after MERS-CoV infection. CoV, human coronavirus; HI, hemagglutination inhibition; MERS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; PRNT90, 90% reduction in plaque reduction neutralization test; RBI, receptor-binding inhibition.