Volume 26, Number 6—June 2020
Research Letter
Co-infection with SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A Virus in Patient with Pneumonia, China
Figure
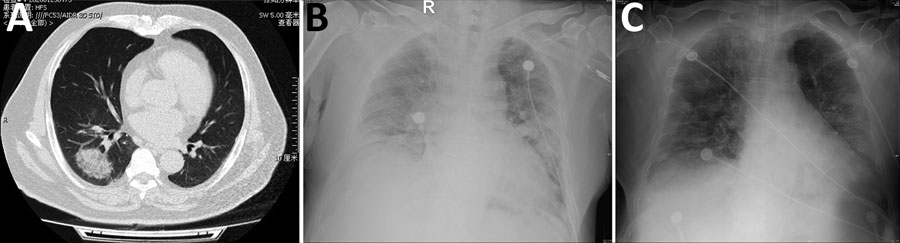
Figure. Radiographs of patient co-infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and influenza A virus, China, 2020. A) Chest computed tomography demonstrating a mass, ground-glass consolidation in the right inferior lobe. B) Chest radiograph showing bilateral diffuse exudative shadows, indicating acute respiratory distress syndrome. C) Chest radiograph showing improved lung fields after 4 days in the intensive care unit.
Page created: May 19, 2020
Page updated: May 19, 2020
Page reviewed: May 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.