Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Research Letter
Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Household Contacts of a Healthcare Provider, Wuhan, China
Figure
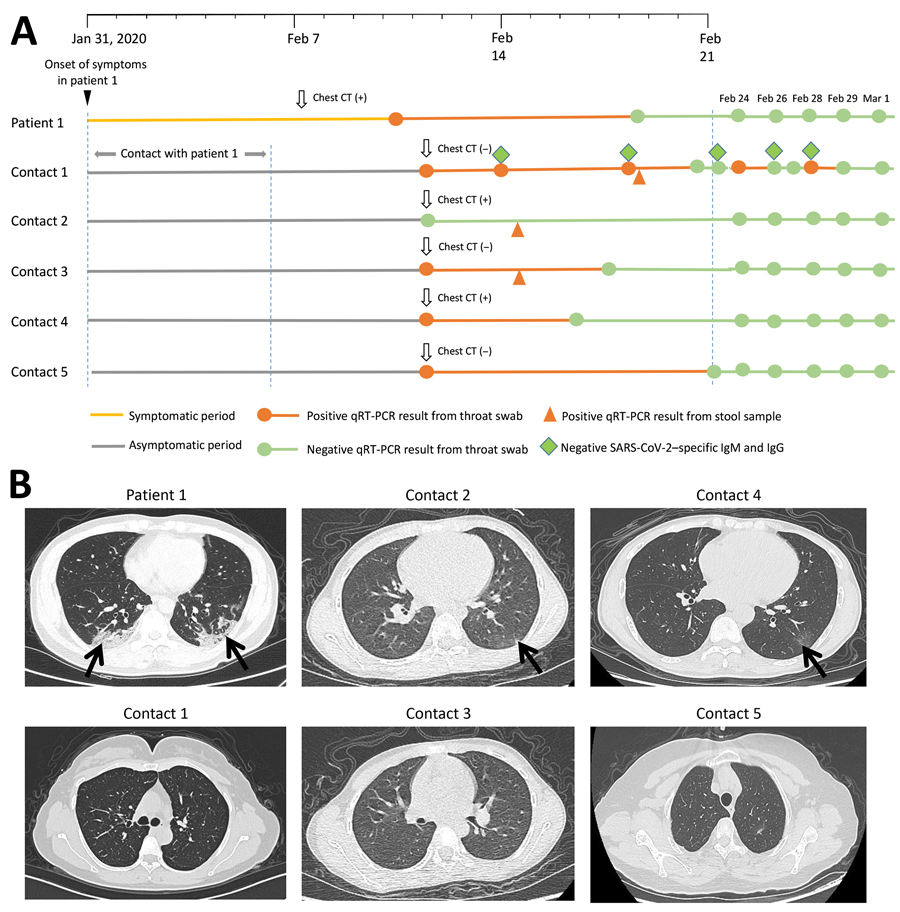
Figure. Timeline and CT images associated with a cluster of SARS-CoV-2 infections in a single household, Wuhan China. A) Timeline of key events, including laboratory tests, associated with SARS-CoV-2 infections in the index patient and 5 asymptomatic household contacts. B) Abnormal chest CT scans showing features consistent with SARS-CoV-2 infection (arrows) observed in the index patient and 2 household contacts (top row), compared with normal CT scans among the 3 other household contacts (bottom row). CT, computed tomography; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: April 24, 2020
Page updated: July 19, 2020
Page reviewed: July 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.