Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Research Letter
Collateral Benefit of COVID-19 Control Measures on Influenza Activity, Taiwan
Figure
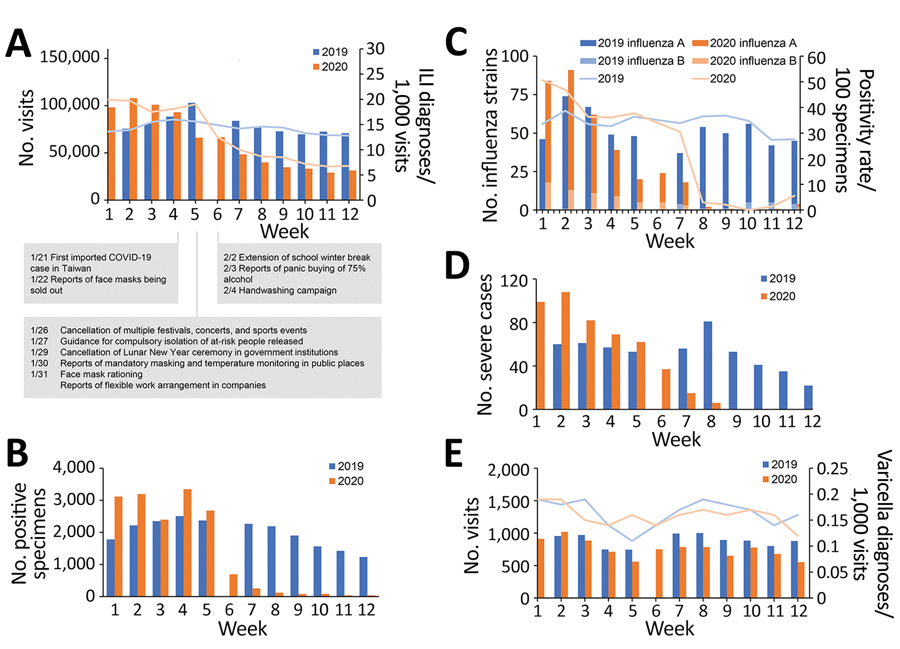
Figure. Influenza and varicella activity in Taiwan during the first 12 weeks of 2020 compared with the corresponding time period in 2019. A) Number of outpatient department visits in which the diagnosis of influenza-like illness (ILI) was made (bars) and the rate of ILI diagnoses per 1,000 visits (lines). Notable dates during the coronavirus disease pandemic are marked along the baseline. B) Number of specimens positive for influenza. C) Number of strains of influenza identified in commissioned laboratories (bars) and the number of positive specimens/total specimens positivity rate (lines). D) Number of laboratory-confirmed influenza cases with severe complications. E) Number of outpatient department visits in which the diagnosis of varicella infection was made (bars) and the rate of varicella diagnoses per 1,000 visits (lines). The 9-day Lunar New Year holiday in week 6 of 2019, when most healthcare service was unavailable, resulted in extreme data, which we excluded from the analysis.