Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Research Letter
Decreased Influenza Incidence under COVID-19 Control Measures, Singapore
Figure
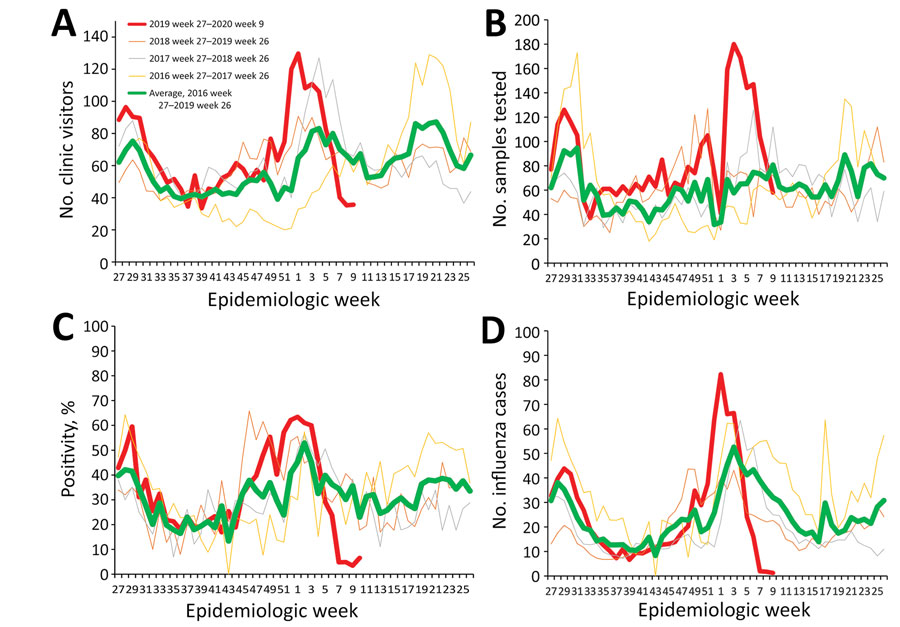
Figure. Indicators of influenza activity during the 2019–20 season (red line) compared with average of the preceding 3 years (green line), Singapore. A) Average number of visits per day to government primary care clinics for influenza-like illnesses, 2016–2020. B) Samples from patients with influenza-like illness tested per week, 2016–2020. C) Influenza positivity, 2016–2020. D) Estimated daily numbers of influenza cases, 2016–2020.
Page created: April 27, 2020
Page updated: July 19, 2020
Page reviewed: July 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.