Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Etymologia
Etymologia: Acanthamoeba
From the Greek akantha (spike/thorn), which was added before amoeba (change) to describe this organism as having a spine-like structure (acanthopodia). This organism is now well-known as Acanthamoeba, an amphizoic, opportunistic, and nonopportunistic protozoan protist widely distributed in the environment.
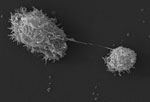
In 1930, it was reported by Castellani in yeast (Cryptococcus pararoseus) culture, and was later (1931) classified as the genus Acanthamoeba by Volkonsky. It was later found to be the etiologic agent of Acanthamoeba granulomatous encephalitis and keratitis in humans. This organism can also cause cutaneous acanthamebiasis in debilitated and immunocompromised patients (Figure).
References
- Castellani A. An amoeba found in culture of yeast: preliminary note. J Trop Med Hyg. 1930;33:160.
- De Jonckheere JF. Ecology of Acanthamoeba. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13(Suppl 5):S385–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khan NA. Acanthamoeba: biology and increasing importance in human health. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2003;16:273–307.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Figure
Cite This ArticleOriginal Publication Date: June 25, 2020
Related Links
Table of Contents – Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Nitika Pradhan, Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology, Bhubaneswar, India
Top