Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Research Letter
Putative Conjugative Plasmids with tcdB and cdtAB Genes in Clostridioides difficile
Figure
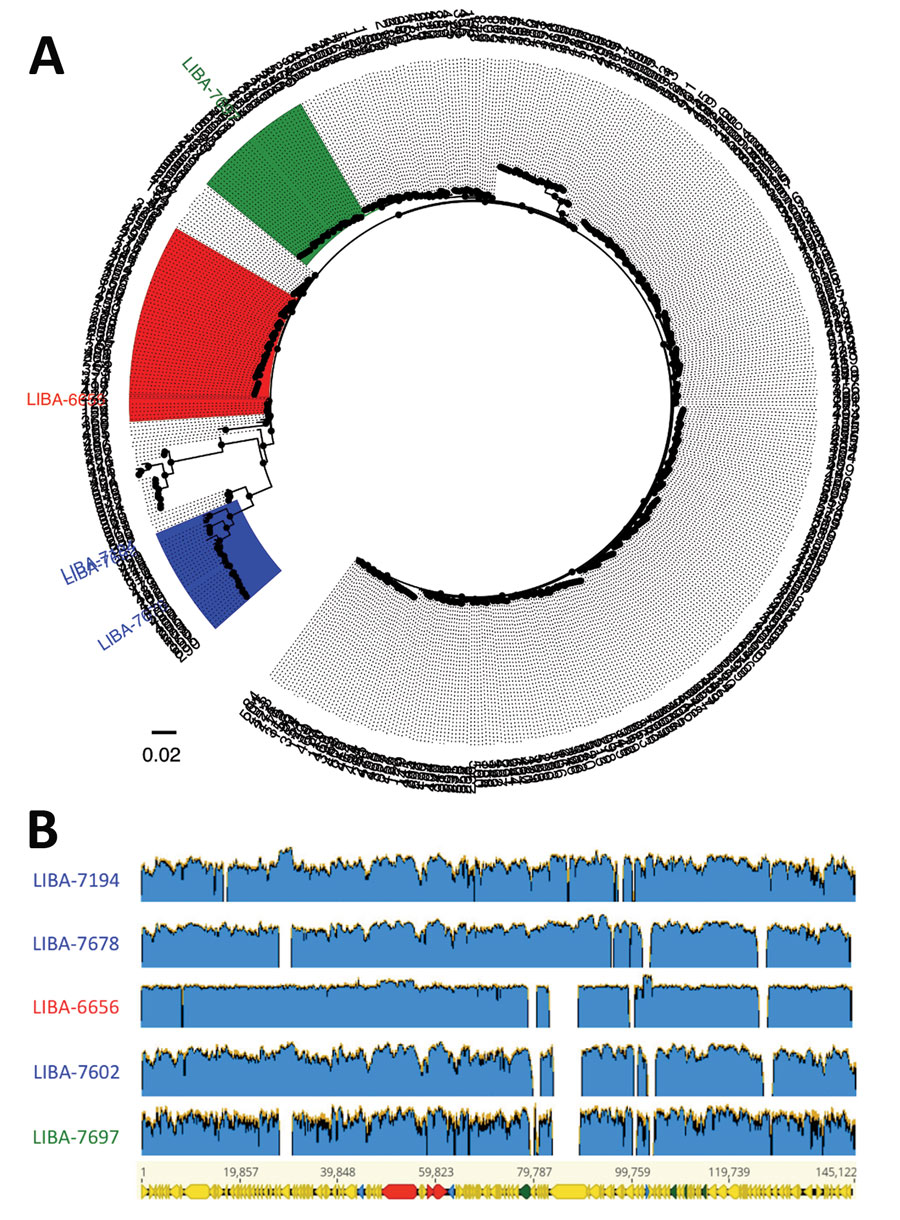
Figure. Multilocus sequence typing–based classification (A) and diversity of extrachromosomal circular sequences (B) of Clostridioides difficile strains with plasmid-encoded toxins. A) FastTree (http://www.microbesonline.org/fasttree) phylogenic tree derived from a MUSCLE (http://www.drive5.com/muscle) alignment of concatenated multilocus sequence typing alleles from all C. difficile sequence types deposited in the PubMLST database (https://pubmlst.org). Tip labels represent sequence types or strain names. Strains from clade C-I are highlighted in blue, from clade 2 in red, and from clade 4 in green. B) This graphic shows short reads from strains LIBA-7194, LIBA-7678, LIBA-7602 (clade C-I, blue), LIBA-6656 (clade 2, red), and LIBA-7697 (clade 4, green) mapped to the plasmid sequence of strain HSJD-312, which was obtained through hybrid PacBio (Pacific Biosciences, https://www.pacb.com) and Illumina (Illumina, https://www.illumina.com) sequencing and therefore used as a reference (145.1 kb, bottom). Arrows in the reference sequence represent annotated coding sequences. Genes for toxins are in red; for transposases, integrases, and recombinases are in blue, and for proteins from a putative conjugation machinery are in green.