Isolation, Sequence, Infectivity, and Replication Kinetics of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Arinjay Banerjee, Jalees A. Nasir
1, Patrick Budylowski
1, Lily Yip, Patryk Aftanas, Natasha Christie, Ayoob Ghalami, Kaushal Baid, Amogelang R. Raphenya, Jeremy A. Hirota, Matthew S. Miller, Allison J. McGeer, Mario Ostrowski, Robert A. Kozak, Andrew G. McArthur, Karen Mossman

, and Samira Mubareka
Author affiliations: McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada (A. Banerjee, J.A. Nasir, K. Baid, A.R. Raphenya, J.A. Hirota, M.S. Miller, A.G. McArthur, K. Mossman); University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (P. Budylowski, N. Christie, A. Ghalami, A.J. McGeer, M. Ostrowski, R.A. Kozak, S. Mubareka); Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto (L. Yip, P. Aftanas, R.A. Kozak, S. Mubareka); Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto (A.J. McGeer)
Main Article
Figure 1
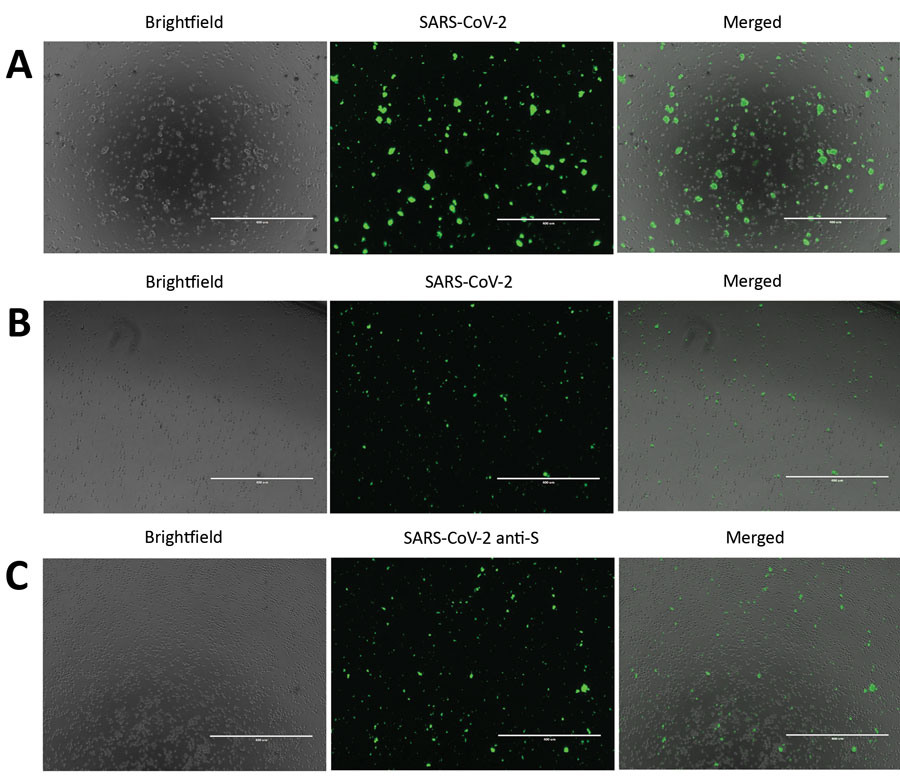
Figure 1. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) protein detection in infected Vero E6 and CD4+ T cells. To detect SARS-CoV-2 protein expression, we infected Vero E6 and CD4+ T cells with SARS-CoV-2 at a multiplicity of infection of 0.1 for 24 h. We immunostained these cells and observed them by using fluorescent microscopy. A) SARS-CoV-2–infected and immunostained Vero E6 cells. B) SARS-CoV-2–infected and immunostained CD4+ T cells. For panels A and B, cells were stained by using an antibody cocktail consisting of SARS-CoV-2 S1 antibody, SARS-CoV-2 N antibody, and diluted serum from a recovered coronavirus disease patient. C) SARS-CoV-2 infected CD4+ T cells immunostained with SARS-CoV-2 S1 antibody (anti-S). Scale bars indicate 400 μm; original magnification ×10.
Main Article
Page created: June 03, 2020
Page updated: August 18, 2020
Page reviewed: August 18, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
