Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Dispatch
Clusters of Coronavirus Disease in Communities, Japan, January–April 2020
Figure 1
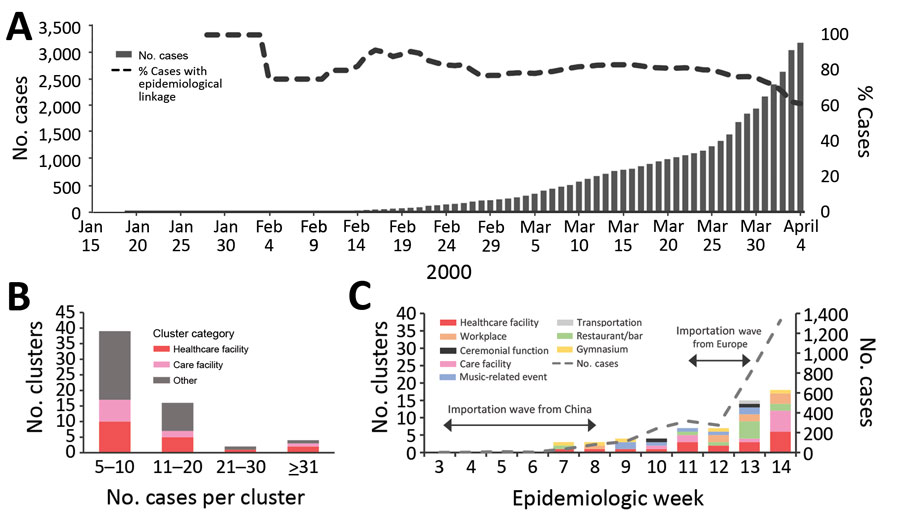
Figure 1. Analysis of 61 clusters of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) cases in communities in Japan, January 15–April 4, 2020. A) Cumulative number of COVID-19 cases, including the proportion of local cases with epidemiologic links to known confirmed cases. B) Distribution of clusters by number of cases in a cluster by category. C) Incidence of clusters of cases according to epidemiologic week as determined by date of confirmation of the first case in a cluster. Incidence of COVID-19 cases (weekly number of newly reported cases) in Japan and timing of two importation waves are also displayed. Epidemiologic week 3 corresponds to January 15, 2020, in panel A. The data and trend of imported cases were previously reported and described by Furuse et al. (8).
References
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al.; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:727–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the mission briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020 [cited 2020 Jun 6]. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the mission briefing on COVID-19—26 February 2020 [cited 2020 May 3]. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-mission-briefing-on-covid-19---26-february-2020
- Pung R, Chiew CJ, Young BE, Chin S, Chen MI, Clapham HE, et al.; Singapore 2019 Novel Coronavirus Outbreak Research Team. Investigation of three clusters of COVID-19 in Singapore: implications for surveillance and response measures. Lancet. 2020;395:1039–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shim E, Tariq A, Choi W, Lee Y, Chowell G. Transmission potential and severity of COVID-19 in South Korea. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;93:339–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ministry of Health. Labour and Welfare. About coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) press conference June 2, 2020 [cited 2020 Jun 6]. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/newpage_00032.html
- Furuse Y, K Ko Y, Saito M, Shobugawa Y, Jindai K, Saito T, et al.; National Task Force for COVID-19 Outbreak in Japan. Epidemiology of COVID-19 outbreak in Japan, January–March 2020. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2020; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jang S, Han SH, Rhee J-Y. Coronavirus disease cluster associated with fitness dance classes, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 May 15 [Epub ahead of print].
- Hamner L, Dubbel P, Capron I, Ross A, Jordan A, Lee J, et al. High SARS-CoV-2 attack rate following exposure at a choir practice—Skagit County, Washington, March 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:606–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prime Minister’s Office of Japan; Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Avoid the “three Cs”! [cited 2020 May 27]. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10900000/000615287.pdf
- Frieden TR, Lee CT. Identifying and interrupting superspreading events—implications for control of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:1059–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.