Volume 27, Number 1—January 2021
Dispatch
Geographic Range of Recreational Water–Associated Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis, United States, 1978–2018
Figure 1
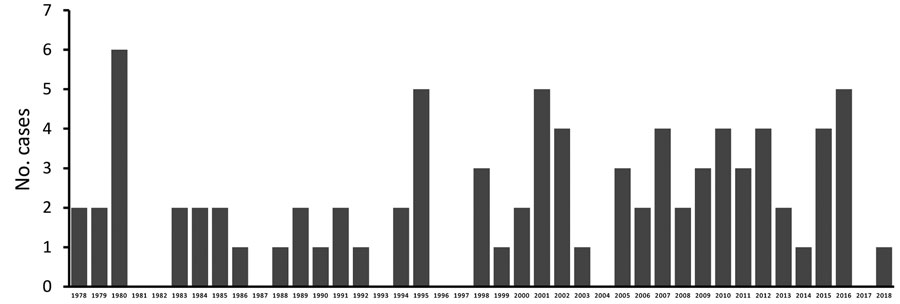
Figure 1. Annual incidence of primary amebic meningoencephalitis cases associated with recreational water exposures, United States, 1978–2018. Negative binomial regression did not detect a trend in the annual incidence of cases (relative risk = 1.015; p = 0.16).
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: September 08, 2020
Page updated: December 21, 2020
Page reviewed: December 21, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.