Volume 27, Number 1—January 2021
Research Letter
Racial and Workplace Disparities in Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2, Baton Rouge, Louisiana, USA
Figure
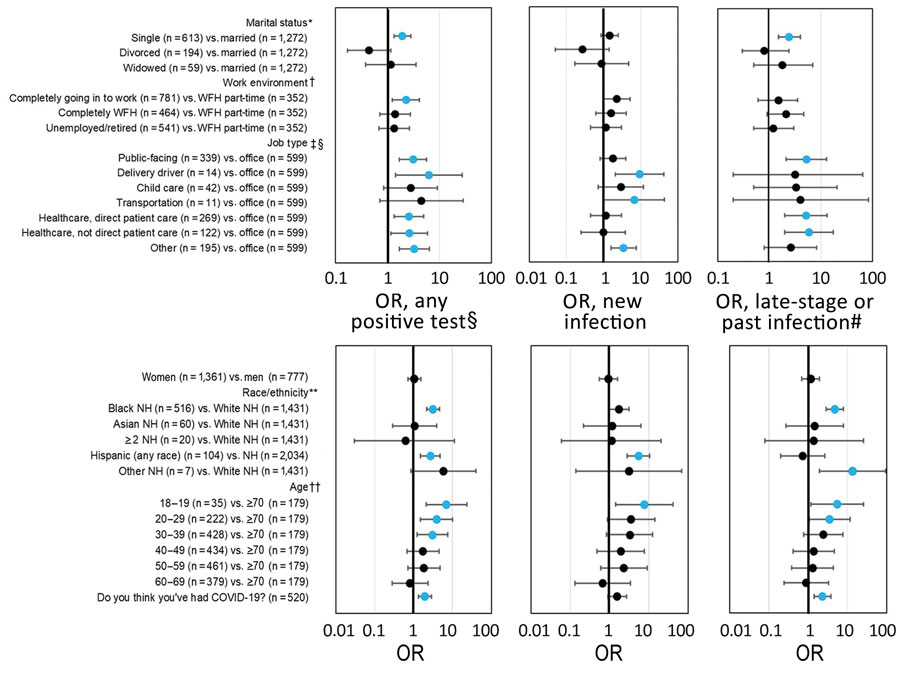
Figure. Odds ratios of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections by marital status, work environment, and job type after phased reopening in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, USA, July 2020. OR from unweighted logistic regression without covariates with Firth correction are shown with 95% CIs. Reference categories’ percent positivity are married (5.0% any infection, 2.3% seroprevalence), WFH part-time (3.7% any infection, 2.0% seroprevalence), and office workers (3.0% any infection, 1.0% seroprevalence). WFH, work from home; NH, non-Hispanic; OR, odds ratio. *Odds of any infection (p = 0.0005) and seroprevalence (p = 0.03) differ by marital status. †Odds of any infection (p = 0.01) differ by work environment. ‡Odds of any infection (p = 0.01) and seroprevalence (p = 0.03) differ by job type. §Six people did not give an answer for job type; none tested positive on any test. Unemployed/retired people (n = 541) are not included in this category. ¶Percentage and OR of any positive test (PCR+ or IgG+). #Percentage and OR of late-stage or past infections (IgG+, regardless of PCR status). **Odds of any infection (p<0.0001) and seroprevalence (p<0.0001) differ by race and ethnicity. ††Odds of any infection (p<0.0001) and seroprevalence (p = 0.0074) differ by age.