Volume 27, Number 11—November 2021
Research
Encephalitis and Death in Wild Mammals at a Rehabilitation Center after Infection with Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus, United Kingdom
Figure 2
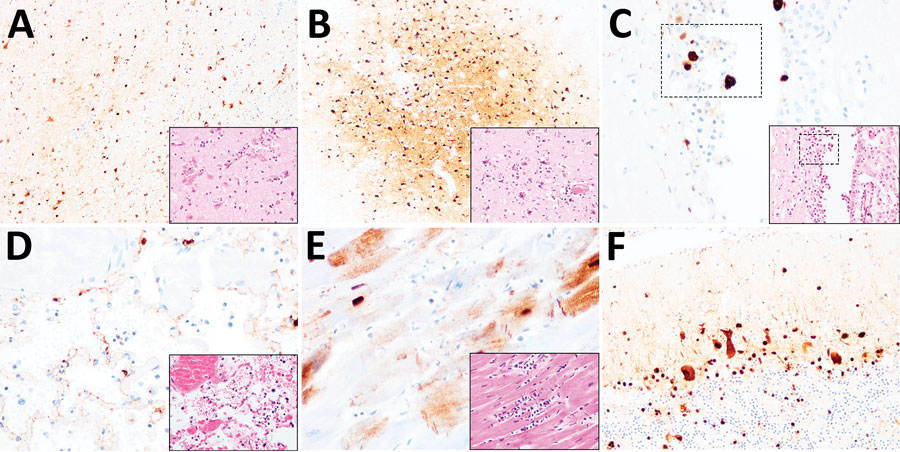
Figure 2. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical examination of the gray seal (Halichoerus grypus), common seal (Phoca vitulina), and red fox (Vulpes vulpes) infected with highly pathogenic avian influenza A subtype H5N8, United Kingdom. Serial tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Immunohistochemical examination was undertaken using anti–influenza A nucleoprotein primary antibody (Statens Serum Institute, https://en.ssi.dk). Insets show histopathologic study results. A) Nonsuppurative polioencephalitis and presence of virus antigens in neurons in the cerebrum, common seal (Phoca vitulina). Original magnification ×10, inset ×40. B) Nonsuppurative polioencephalitis with neuronophagia and association of virus antigens, red fox. Original magnification ×10, inset ×40. C) Ependymal necrosis and the association of virus antigens, fox. Original magnification and inset ×40; area of interest also shown. D) Diffuse alveolar damage and presence of virus in type I alveolar pneumocytes, red fox. Original magnification and inset ×40. E) Cardiomyonecrosis associated with virus antigens in cardiomyocytes, red fox. Original magnification and inset ×40. F) Virus antigens in granular and molecular layer of the cerebellum, red fox. Original magnification ×20, inset ×40. Serial tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Immunohistochemical examination was undertaken using anti–influenza A nucleoprotein primary antibody (Statens Serum Institute, https://en.ssi.dk). Insets show histopathologic study results.