Volume 27, Number 12—December 2021
Research Letter
Postmortem Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in Mouse Lung Tissue
Figure
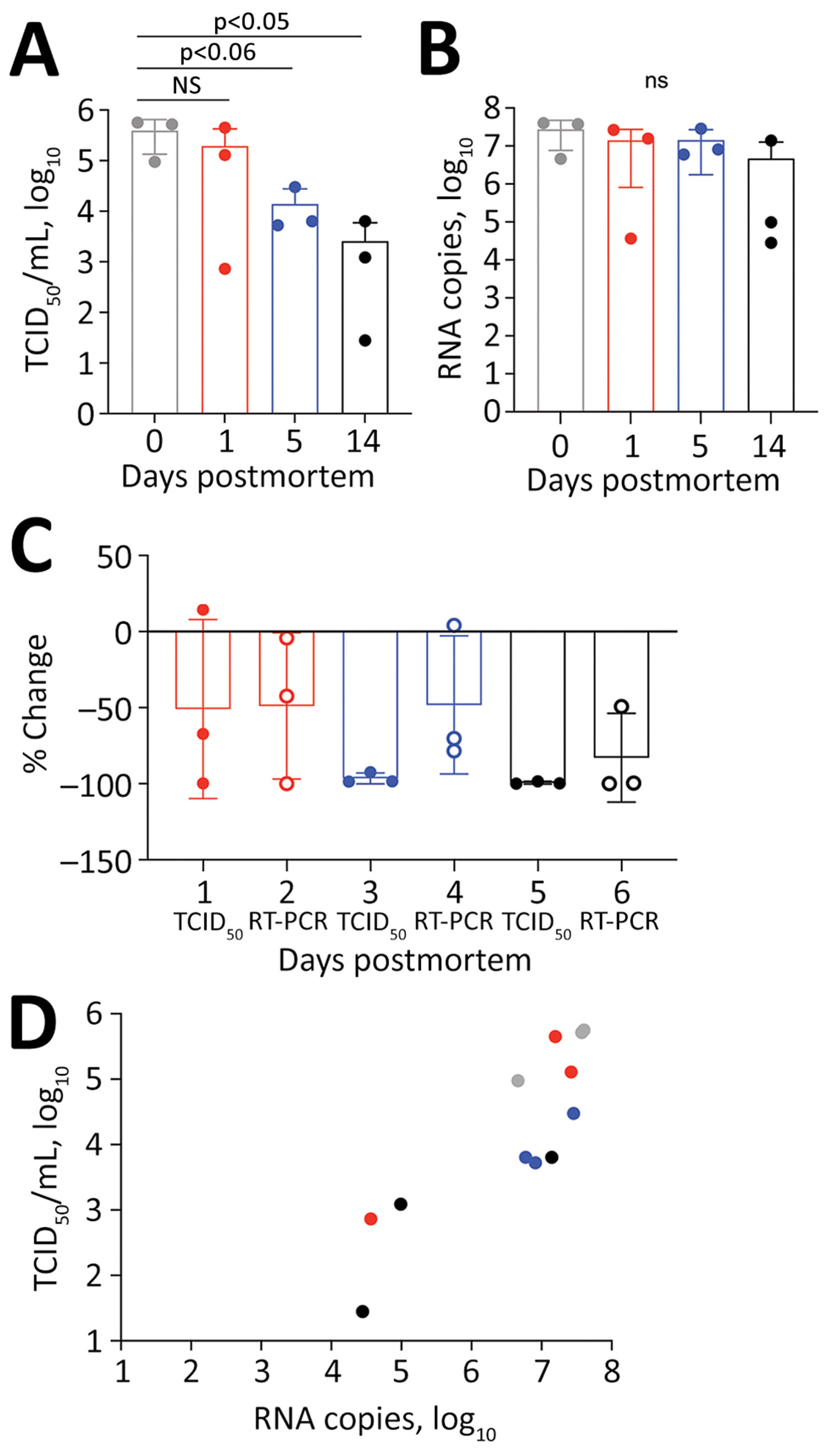
Figure. Postmortem stability of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in mouse lung tissue. A) Infectious virus measured by TCID50 of VeroE6 cells. B) Viral RNA measured by copies of N gene detected by RT-PCR. C) Percentage change compared with day 0. D) Correlation between infectious virus and viral RNA. R2 = 0.51; F = 0.005 by analysis of variance. NS, not significant; RT-PCR, reverse transcription PCR; TCID50, 50% tissue culture infectious dose.
Page created: September 21, 2021
Page updated: November 19, 2021
Page reviewed: November 19, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.