Volume 27, Number 2—February 2021
Dispatch
Human Tacheng Tick Virus 2 Infection, China, 2019
Figure 1
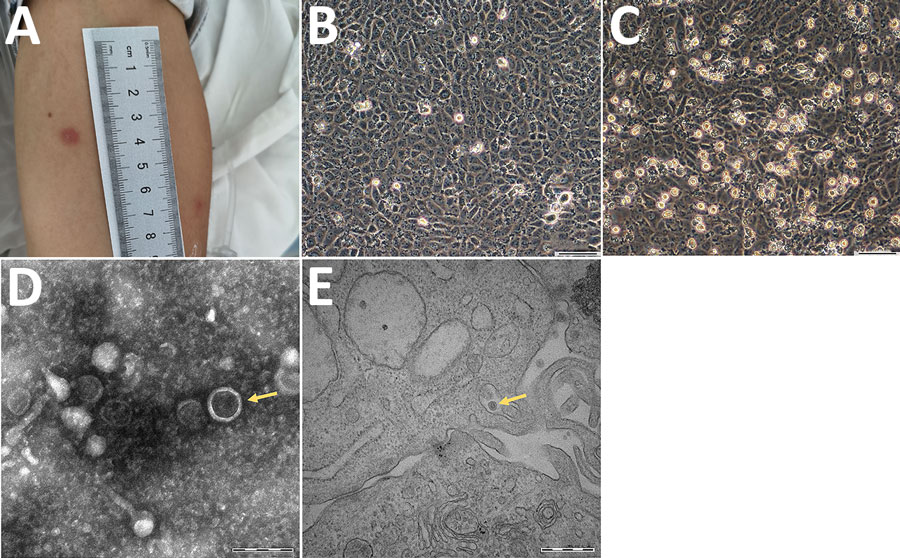
Figure 1. Clinical and morphological features of Tacheng tick virus 2 in a patient, China. A) Erythema at the site of tick bite on the anterior surface of the patient’s left arm. B) Human hepatocellular carcinoma (SMMC-7721) cells without TcTV-2 infection; magnification × 100. Scale bar indicates 50 μm. C) TcTV-2–infected SMMC-7721 cells showing cytopathic effects visible by light microscopy; magnification × 100. Scale bar indicates 50 μm. D) Negatively stained virions purified from TcTV-2–infected SMMC-7721 cells (arrows); magnification × 25,000. Scale bar indicates 200 nm. E) Transmission electron microscopy image of TcTV-2–infected SMMC-7721 cells (arrows); magnification × 50,000. Scale bar indicates 500 nm. TcTV-2, Tacheng tick virus 2.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.