Volume 27, Number 2—February 2021
Dispatch
Novel Arterivirus Associated with Outbreak of Fatal Encephalitis in European Hedgehogs, England, 2019
Figure 1
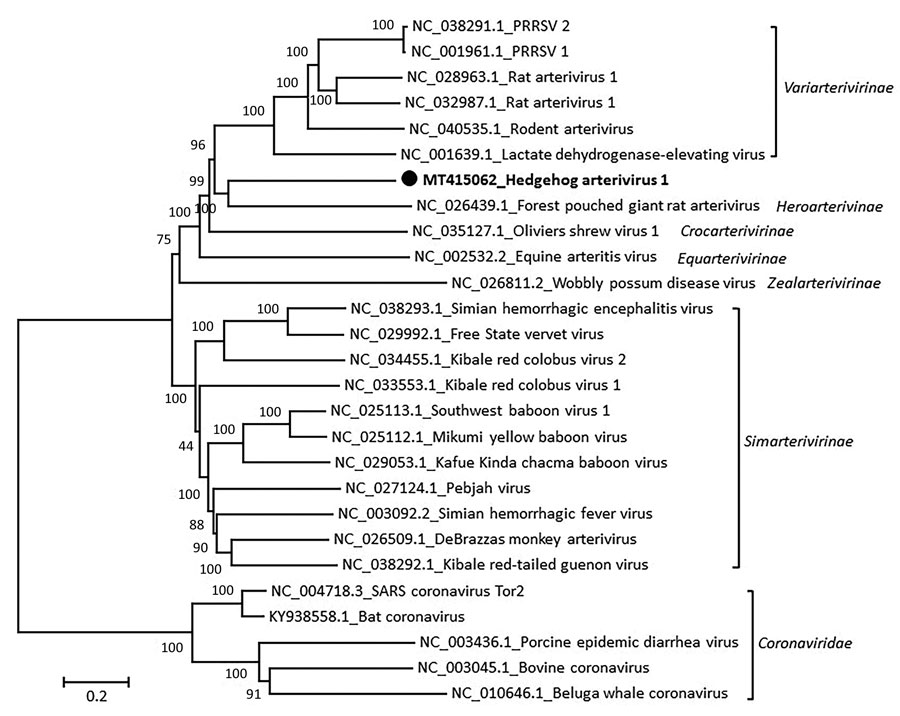
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of the coding sequence of hedgehog arterivirus 1. The virus genome was aligned by using the MegAlign software of the DNASTAR Lasergene Core Suite (DNASTAR, Inc., https://www.dnastar.com), and phylogenetic analysis was performed by using MEGA 5.2 software (https://www.megasoftware.net). The rooted tree was constructed by using the neighbor-joining method and 1,000 bootstrap replications. Each virus on the tree is represented by its GenBank accession number and name. Designation of subfamilies was conducted as outlined in the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses 2018 release (https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports). Coronaviruses are included as an outgroup. Solid black circle and bold indicate strain detected in this study. Numbers along branches are bootstrap values. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.