Volume 27, Number 3—March 2021
Research
Genomic Characterization of hlyF-positive Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli, Italy and the Netherlands, 2000–2019
Figure 3
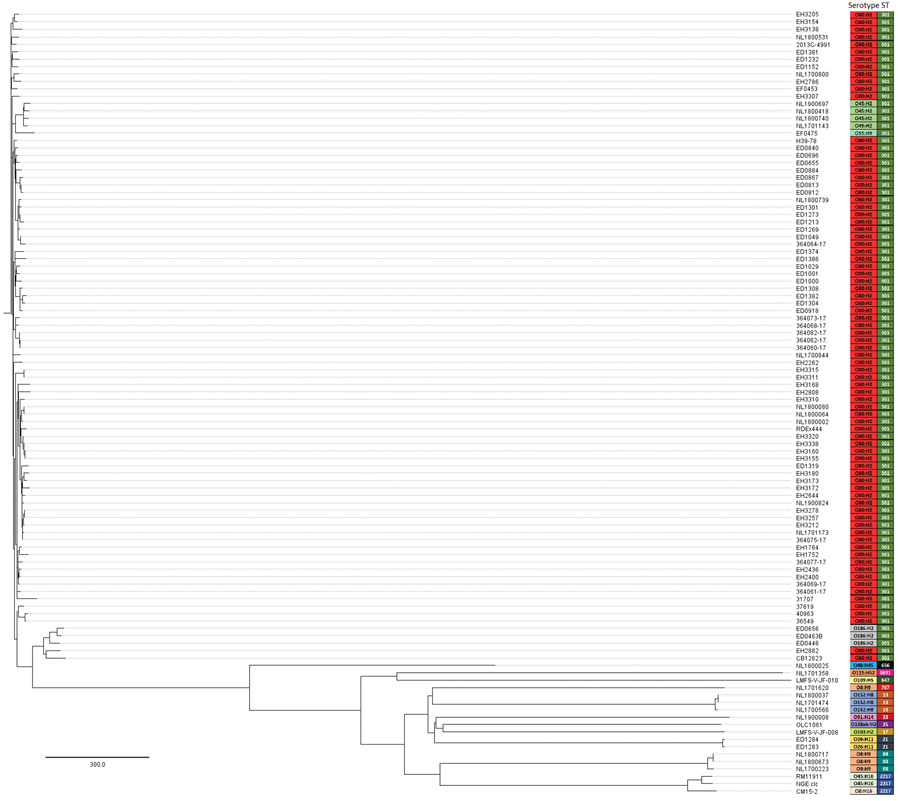
Figure 3. Cluster analysis by core genome multilocus sequence typing of Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli strains harboring extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli–associated virulence genes. The analysis also included the RDEx444 strain from France; 2 Shiga toxin–producing E. coli O80:H2 strains negative for the pR444_A plasmid (i.e., ED0867 and ED1301); and the set of 50 E. coli genomes positive either for stx or hlyF genes, downloaded from GenBank or RefSeq (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/RefSeq). Each entry on the phylogenetic tree indicates the strain name, corresponding serotype, and sequence type. Colors indicates serotype and sequence type. Scale bar indicates the number of allelic differences.
Page created: December 23, 2020
Page updated: February 21, 2021
Page reviewed: February 21, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.