Volume 27, Number 5—May 2021
Dispatch
Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children, Chile, May–August 2020
Figure
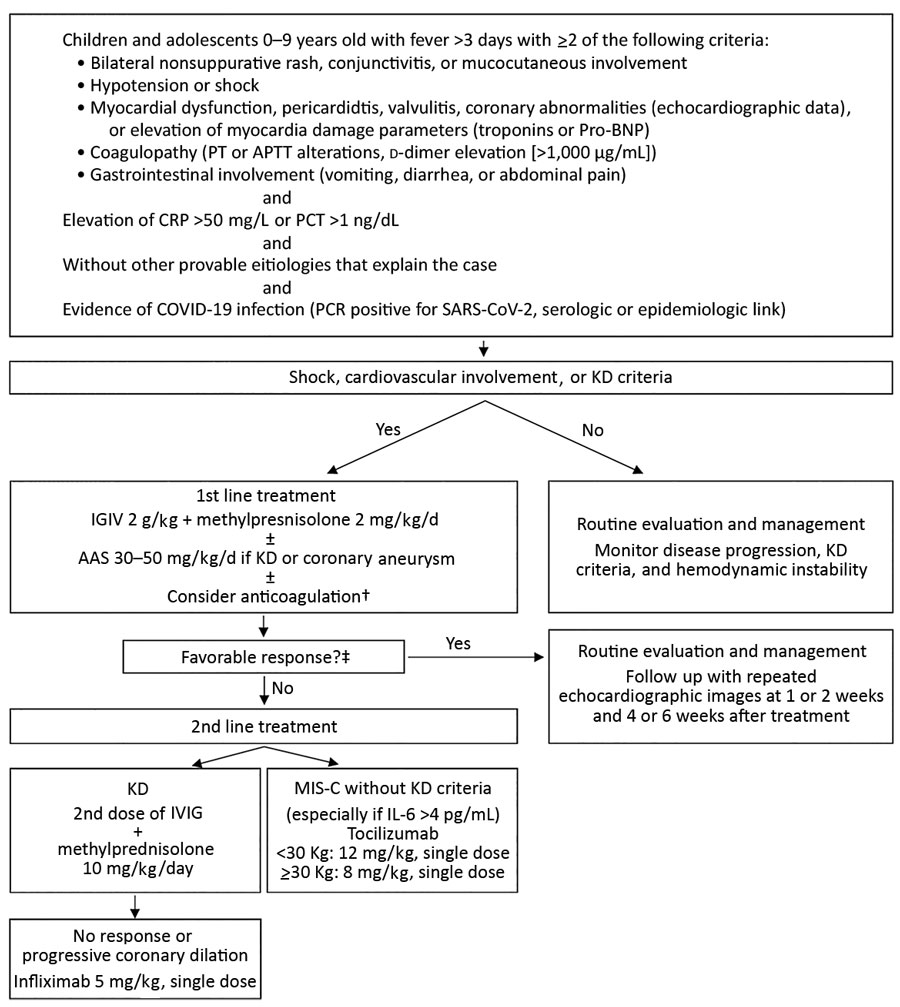
Figure. Treatment algorithm for children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19, Chile, May–August 2020. †Prophylactic anticoagulation was considered if D-dimer was >1,000 ng/dL or progressively increasing: treatment was 1 mg/kg/d of low molecular weight heparin (Enoxaparin). When thrombosis was suspected or confirmed, the dose was increased to 1 mg/kg every 12 hours and adjusted with anti-Xa factor activity. ‡Favorable response was considered absence of fever for 48 hours, hemodynamic stability, and improvement of inflammatory parameters. AAS, acetylsalicylic acid; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; COVID-19, coronavirus disease; CRP, C-reactive protein; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; KD, Kawasaki disease; MIS-C, pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with coronavirus disease; PCT, procalcitonin; pro-BNP, pro–brain natriuretic peptide; PT, prothrombin time; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.