Volume 27, Number 6—June 2021
Research Letter
Changing Molecular Epidemiology of Hepatitis A Virus Infection, United States, 1996–2019
Figure
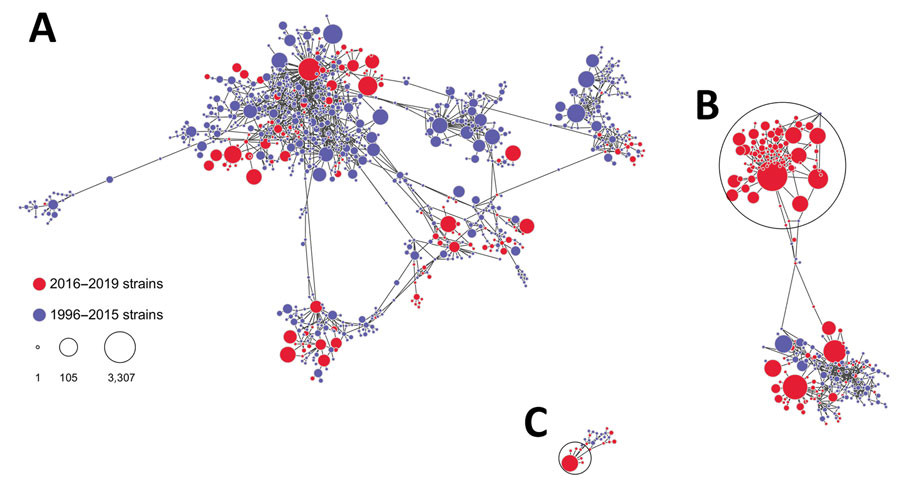
Figure. Genetic relatedness among hepatitis (HAV) strains, United States, 1996–2019. A) IA strains; B) IB strains; C) IIIA strains. Nodes represent HAV strains, and the size of node is proportional to the frequency of the strain; larger nodes denote more frequent detection. Distance between nodes approximates genetic closeness of HAV strains. Genetic clusters of closely related HAV strains encompassing a large fraction of all strains in HAV genotypes IB and IIIA are circled. Visualization created by using Gephi software (https://gephi.org).
Page created: March 18, 2021
Page updated: May 18, 2021
Page reviewed: May 18, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.