Volume 27, Number 6—June 2021
Synopsis
Pertactin-Deficient Bordetella pertussis, Vaccine-Driven Evolution, and Reemergence of Pertussis
Figure 2
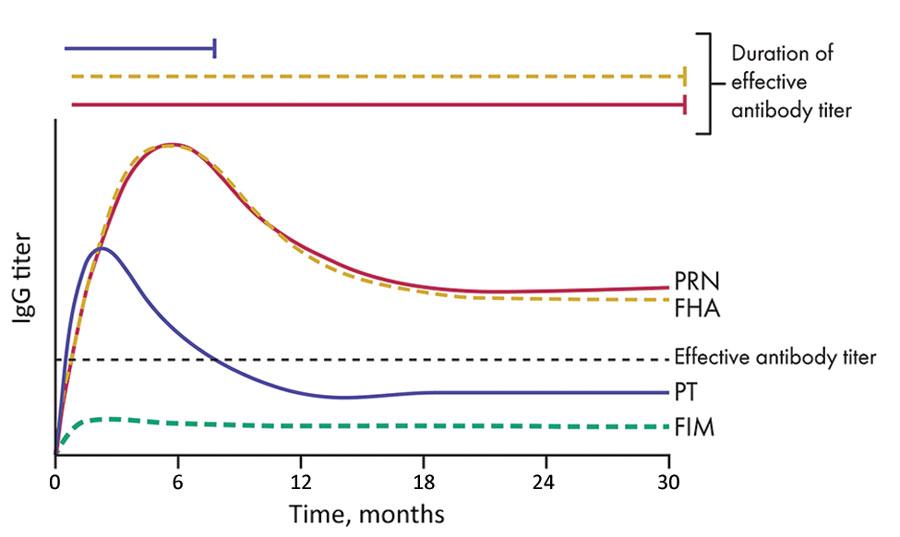
Figure 2. Differential decay of antibodies against acellular pertussis vaccine antigens and their effective capacity for protection. Antibodies against PRN and FHA remain at relatively higher titers for a longer period. However, PT-specific antibodies decrease to low titers rapidly. A consistently low level of antibodies against FIM is induced. Solid lines indicate antibodies that have high protective capacity, and dotted lines indicate antibodies that had low protective capacity. Only PRN antibodies are highly protective and persist at high titers for years. FHA, filamentous hemagglutinin, FIM, fimbriae; PT, pertussis toxin; PRN, pertactin.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: March 05, 2021
Page updated: May 18, 2021
Page reviewed: May 18, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.