Neurologic Disease after Yellow Fever Vaccination, São Paulo, Brazil, 2017–2018
Ana Freitas Ribeiro
1, Bruno Fukelmann Guedes
1
, Jamal M.A.H. Sulleiman, Francisco Tomaz Meneses de Oliveira, Izabel Oliva Marcilio de Souza, Juliana Silva Nogueira, Rosa Maria Nascimento Marcusso, Eder Gatti Fernandes, Guilherme Sciascia do Olival, Pedro Henrique Fonseca Moreira de Figueiredo, Ana Paula Rocha Veiga, Flávia Esper Dahy, Natália Nasser Ximenes, Lecio Figueira Pinto, José Ernesto Vidal, and Augusto Cesar Penalva de Oliveira
Author affiliations: Universidade Nove de Julho, São Paulo, Brazil (A.F. Ribeiro); Instituto de Infectologia Emílio Ribas, São Paulo (A.F. Ribeiro, J.M.A.H. Sulleiman, R.M. Nascimento Marcusso, G. Sciascia do Olival, A.P. Rocha Veiga, F. Esper Dahy, J.E. Vidal, A.C. Penalva de Oliveira); Hospital das Clínicas, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo (B.F. Guedes, I.O. Marcilio de Souza, P.H.F. Moreira de Figueiredo, N. Nasser Ximenes, L. Figueira Pinto, J. Ernesto Vidal); Irmandade Santa Casa de Misericórdia de São Paulo, São Paulo (F.T. Meneses de Oliveira); Instituto Adolfo Lutz, São Paulo (J. Silva Nogueira); Centro de Vigilância Epidemiológica Prof. Alexandre Vranjac, São Paulo (E. Gatti Fernandes)
Main Article
Figure 3
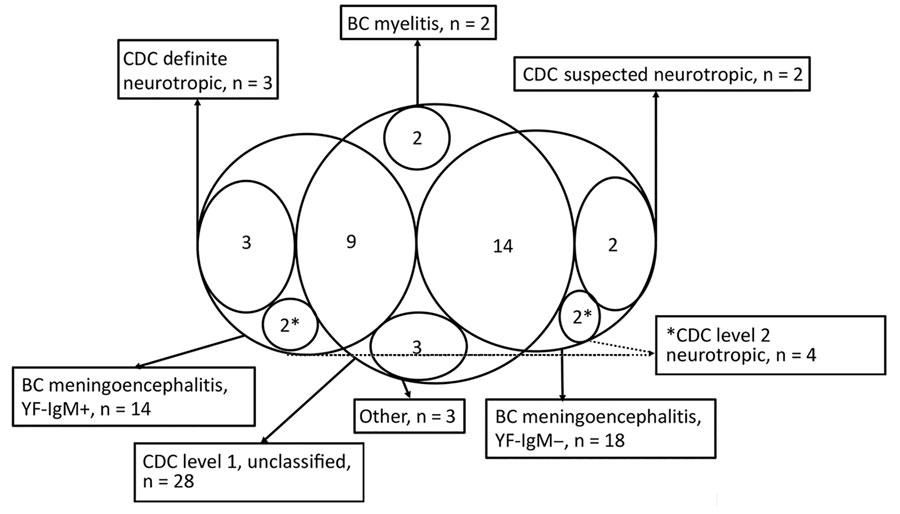
Figure 3. Classification of cases of yellow fever vaccine–associated neurologic disease, São Paulo, Brazil, 2017–2018. Excluded cases, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis cases, and Guillain-Barré syndrome cases not shown. The area with n= 9 represents the intersection between the group "BC meningoencephalitis, YF-IgM+ (reactive CSF-YF-IgM)” and “CDC level 1, unclassified.” The area with n = 14 represents the intersection between the group "BC meningoencephalitis, YF-IgM– (nonconfirmed)" and "CDC level 1, unclassified." BC, Brighton Collaboration criteria; CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria; level 1 unclassified, level 1 neurologic disease not classifiable as level 2; level 2 neurotropic, level 2 neurotropic disease not further classified as suspected or definite neurotropic disease; other, includes atypical yellow fever vaccine–associated neurologic disease (optic neuritis, n = 1; ataxia, n = 1; opsoclonus-myoclonus-ataxia syndrome, n = 1); +, positive.
Main Article
Page created: April 12, 2021
Page updated: May 18, 2021
Page reviewed: May 18, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
