Seroprevalence of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 IgG in Juba, South Sudan, 20201
Kirsten E. Wiens, Pinyi Nyimol Mawien, John Rumunu, Damien Slater, Forrest K. Jones, Serina Moheed, Andrea Caflisch, Bior K. Bior, Iboyi Amanya Jacob, Richard Lino Lako, Argata Guracha Guyo, Olushayo Oluseun Olu, Sylvester Maleghemi, Andrew Baguma, Juma John Hassen, Sheila K. Baya, Lul Deng, Justin Lessler, Maya N. Demby, Vanessa Sanchez, Rachel Mills, Clare Fraser, Richelle C. Charles
2, Jason B. Harris
2, Andrew S. Azman
3
, and Joseph F. Wamala
3
Author affiliations: Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA (K.E. Wiens, F.K. Jones, J. Lessler, M.N. Demby, A.S. Azman); Republic of South Sudan Ministry of Health, Juba, South Sudan (P.N. Mawien, J. Rumunu, B.K. Bior, I.A. Jacob, R.L. Lako, L. Deng); Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA (D. Slater, S. Moheed, V. Sanchez, R. Mills, C. Fraser, R.C. Charles, J.B. Harris); International Organization for Migration, Juba (A. Caflisch); World Health Organization, Juba (A.G. Guyo, O.O. Olu, S. Maleghemi, A. Baguma, J.J. Hassen, S.K. Baya, J.F. Wamala); Kabale University School of Medicine, Kabale, Uganda (A. Baguma); Harvard Medical School, Boston (R.C. Charles, J.B. Harris); Médecins Sans Frontières, Geneva, Switzerland (A.S. Azman); Institute of Global Health, Geneva (A.S. Azman)
Main Article
Figure 2
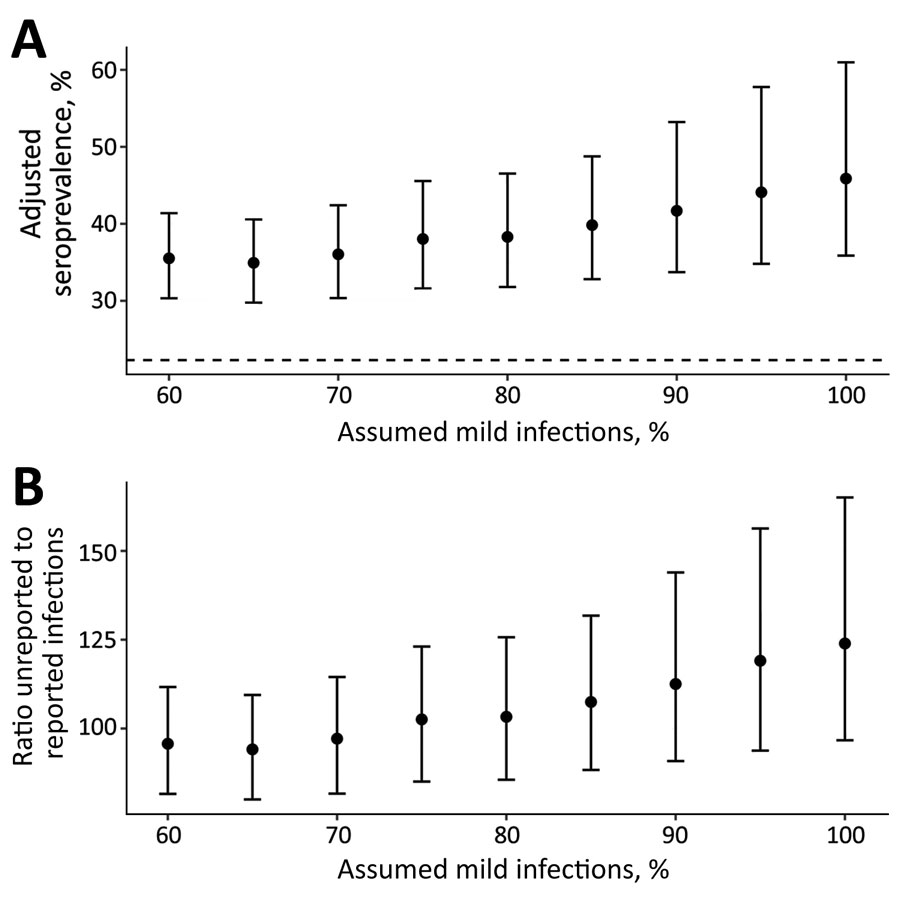
Figure 2. Effects of changing percentage of assumed mild cases in the population on adjusted seroprevalence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 IgG in Juba, South Sudan. A) Mean adjusted seroprevalence; B) ratio of unreported to reported infections. Error bars represent 95% credible intervals. Dashed line in panel A represents unadjusted seropositivity at 22.3%. Unreported infections in panel B based on 1,873 confirmed coronavirus disease cases in Juba (as of August 31, 2020) and an approximate population of 510,000 in Juba. The x-axis in both panels indicates percentage of mild cases included in the synthetic positive control dataset used to estimate assay sensitivity.
Main Article
Page created: March 25, 2021
Page updated: May 18, 2021
Page reviewed: May 18, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
