Volume 27, Number 7—July 2021
Dispatch
Cluster of Oseltamivir-Resistant and Hemagglutinin Antigenically Drifted Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Viruses, Texas, USA, January 2020
Figure 1
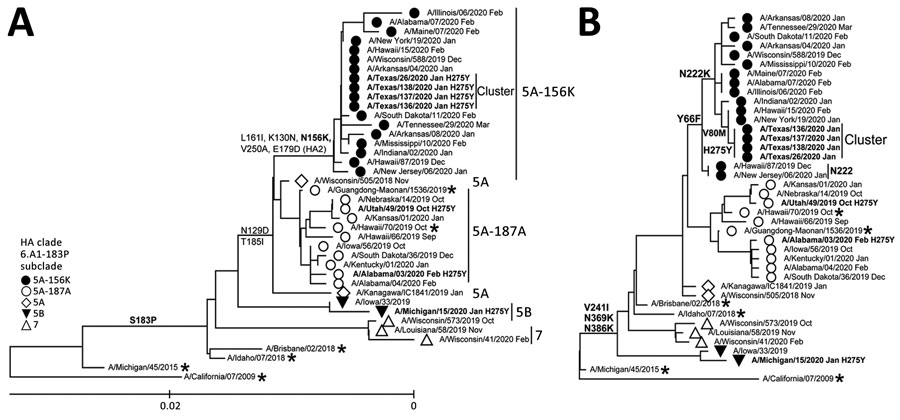
Figure 1. Evolutionary relationships of the HA (A) and NA (B) genes of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses circulating in the United States during the 2019–20 influenza season compared with reference viruses. We generated phylogenetic trees using MEGA software version 10.1.8 (http://www.megasoftware.net) and the bootstrap method (1,000 replications). We computed evolutionary distances by using the maximum composite likelihood model. Analysis included 40 representative A(H1N1)pdm09 HA and NA gene sequences. Boldface indicates oseltamivir-resistant viruses carrying NA-H275Y substitution; asterisks indicate vaccine viruses. A/California/07/2009 virus (the first A(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine) is used as a reference for ancestry (root) and numbering. Scale bar represents nucleotide substitutions per site. HA, hemagglutinin; NA, neuraminidase.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.