Volume 28, Number 1—January 2022
Research
New Sequence Types and Antimicrobial Drug–Resistant Strains of Streptococcus suis in Diseased Pigs, Italy, 2017–2019
Figure 1
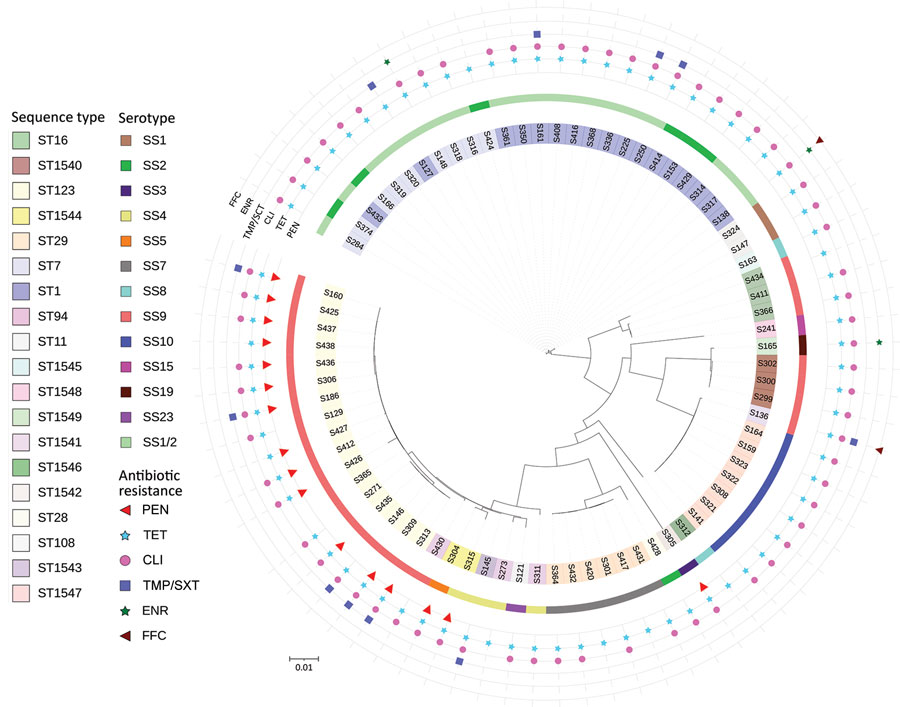
Figure 1. Circular phylogenetic tree containing 78 Streptococcus suis isolates from diseased pigs, Italy, 2017–2019. The tree was inferred by using the iTOL interactive user interface (https://itol.embl.de). Shading over tip labels indicates sequence types. The serotypes of each isolate are also shown. The antimicrobial-resistant molecules are annotated by colors and shapes. Scale bar indicates substitutions per site. CLI, clindamycin; ENR, enrofloxacin; FFC, florfenicol; PEN, penicillin; ST, sequence type; TET, tetracycline; TMP/SXT, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.
Page created: November 10, 2021
Page updated: December 20, 2021
Page reviewed: December 20, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.