Volume 28, Number 10—October 2022
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Demographic and Socioeconomic Factors Associated with Fungal Infection Risk, United States, 2019
Figure 6
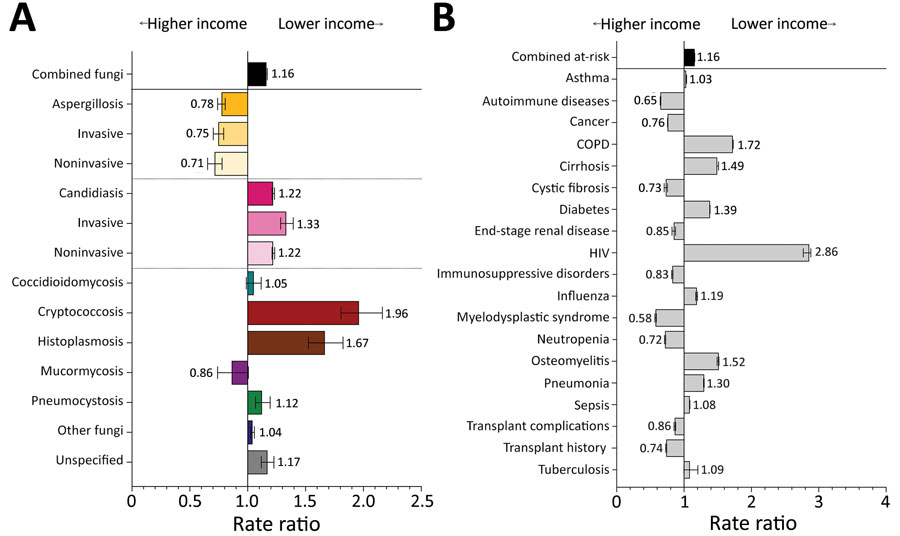
Figure 6. Comparison of rate ratios for fungal infections and risk conditions by income among hospitalized patients, United States, 2019. A) Diagnosed fungal infections; B) risk conditions. Income levels were determined by postal code; patients from postal codes with incomes in the highest quartile were compared with patients from postal codes with incomes in the lowest quartile. Bars and numerals indicated rate ratios; error bars indicate 95% CIs. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Page created: August 11, 2022
Page updated: September 21, 2022
Page reviewed: September 21, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.