Volume 28, Number 3—March 2022
Research
Spatiotemporal Analyses of 2 Co-Circulating SARS-CoV-2 Variants, New York State, USA
Figure 4
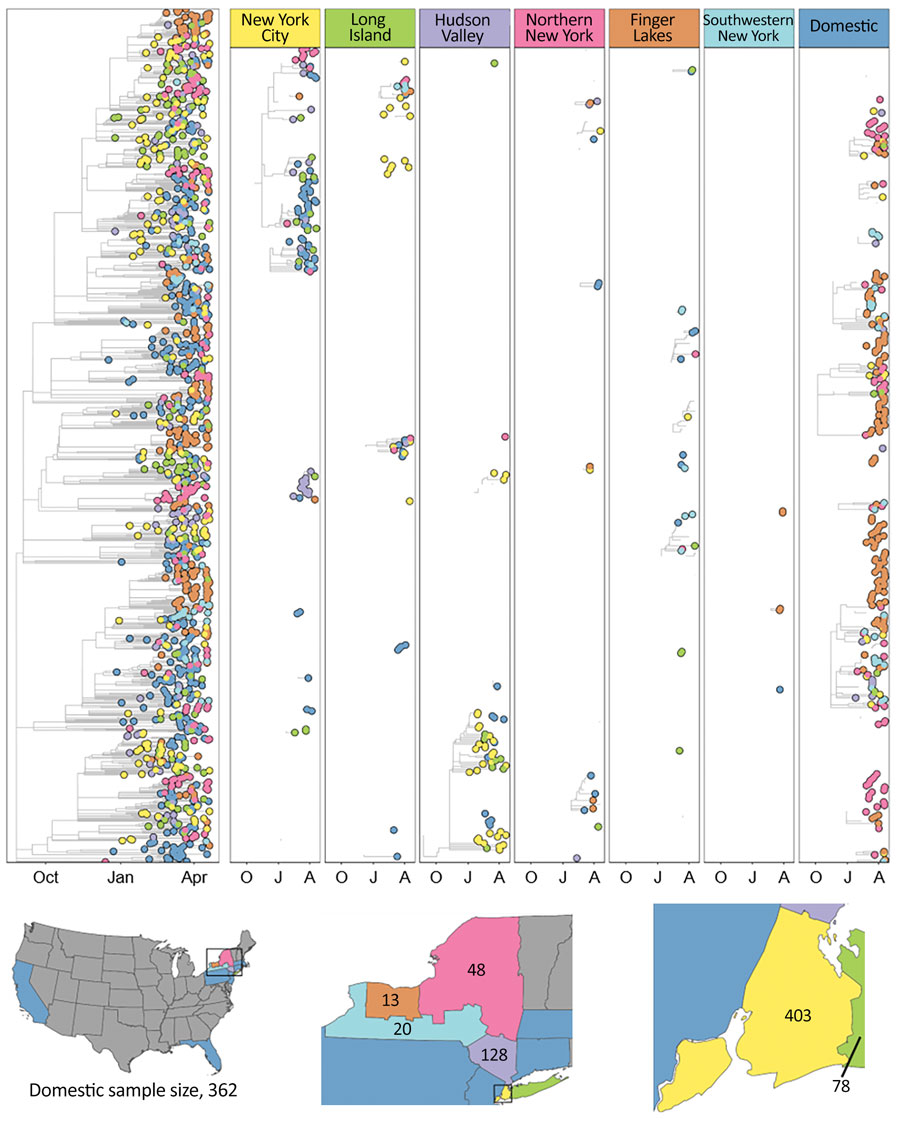
Figure 4. Time-calibrated phylogeny of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 variant B.1.1.7, New York and other states, USA, December 2020–April 2021. Left panel represents a maximum-likelihood phylogeny of 1,195 genomes from New York and other states generated in IQTree 1.6.12 (20) with timescale inferred by TreeTime 0.7.6 (22) and ancestral state reconstruction performed in BEAST 2.6.2 (23). The tree was rooted with a P.1 genome (not shown). Faceted panels indicate the source of B.1.1.7 introductions into different regions of New York and other states (domestic). Only introductions supported by an ancestral state probability of >0.7 are shown. Bottom panel shows locations sampled and sample sizes. A, April; J, January; O, October.
References
- Grubaugh ND, Hodcroft EB, Fauver JR, Phelan AL, Cevik M. Public health actions to control new SARS-CoV-2 variants. Cell. 2021;184:1127–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lauring AS, Hodcroft EB. Genetic variants of SARS-CoV-2—what do they mean? JAMA. 2021;325:529–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frampton D, Rampling T, Cross A, Bailey H, Heaney J, Byott M, et al. Genomic characteristics and clinical effect of the emergent SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 lineage in London, UK: a whole-genome sequencing and hospital-based cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:1246–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kidd M, Richter A, Best A, Cumley N, Mirza J, Percival B, et al. S-variant SARS-CoV-2 lineage B1.1.7 is associated with significantly higher viral load in samples tested by TaqPath polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 2021;223:1666–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Planas D, Bruel T, Grzelak L, Guivel-Benhassine F, Staropoli I, Porrot F, et al. Sensitivity of infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants to neutralizing antibodies. Nat Med. 2021;27:917–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tegally H, Wilkinson E, Giovanetti M, Iranzadeh A, Fonseca V, Giandhari J, et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa. Nature. 2021;592:438–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- West AP Jr, Wertheim JO, Wang JC, Vasylyeva TI, Havens JL, Chowdhury MA, et al. Detection and characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.526 in New York. Nat Commun. 2021;12:4886. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Epidemiological update: variants of SARS-CoV-2 in the Americas. 2021 Mar [cited 2021 Dec 9]. https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/53382
- Thompson CN, Hughes S, Ngai S, Baumgartner J, Wang JC, McGibbon E, et al.; PhD1. PhD1. PhD1. Rapid emergence and epidemiologic characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.526 variant—New York City, New York, January 1–April 5, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:712–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Annavajhala MK, Mohri H, Wang P, Nair M, Zucker JE, Sheng Z, et al. Emergence and expansion of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.526 after identification in New York. Nature. 2021;597:703–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alpert T, Brito AF, Lasek-Nesselquist E, Rothman J, Valesano AL, MacKay MJ, et al. Early introductions and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7 in the United States. Cell. 2021;184:2595–2604.e13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jung I, Kulldorff M, Richard OJ. A spatial scan statistic for multinomial data. Stat Med. 2010;29:1910–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kulldorff M. Software for the spatial and space-time scan statistics. 2018 [2021 Dec 9]. http://www.satscan.org
- Desjardins MR, Hohl A, Delmelle EM. Rapid surveillance of COVID-19 in the United States using a prospective space-time scan statistic: Detecting and evaluating emerging clusters. Appl Geogr. 2020;118:
102202 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Takahashi K, Kulldorff M, Tango T, Yih K. A flexibly shaped space-time scan statistic for disease outbreak detection and monitoring. Int J Health Geogr. 2008;7:14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shepard D. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. 1968 Jan 1 [cited 2021 Jun 8]. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=800186.810616
- Rogerson PA, Plane DA. Geographical analysis of population: with applications to planning and business. International edition. Hoboken (New Jersey): John Wiley and Sons Ltd; 1994.
- Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:772–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nguyen L-T, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ. IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32:268–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Minh BQ, Nguyen MAT, von Haeseler A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:1188–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sagulenko P, Puller V, Neher RA. TreeTime: Maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. Virus Evol. 2018;4:
vex042 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Bouckaert R, Vaughan TG, Barido-Sottani J, Duchêne S, Fourment M, Gavryushkina A, et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLOS Comput Biol. 2019;15:
e1006650 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Rambaut A, Drummond AJ, Xie D, Baele G, Suchard MA. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst Biol. 2018;67:901–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yu G, Smith DK, Zhu H, Guan Y, Lam TT-Y. ggtree: an r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol Evol. 2017;8:28–36. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Neher R. The virus is under increasing selection pressure. Max-Planck-Gesellschaft. 2021 [cited 2021 Aug 10]. https://www.mpg.de/16371358/coronavirus-variants
- Campbell F, Archer B, Laurenson-Schafer H, Jinnai Y, Konings F, Batra N, et al. Increased transmissibility and global spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern as at June 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26:
2100509 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.