Volume 28, Number 4—April 2022
Dispatch
Infectious Toscana Virus in Seminal Fluid of Young Man Returning from Elba Island, Italy
Figure 1
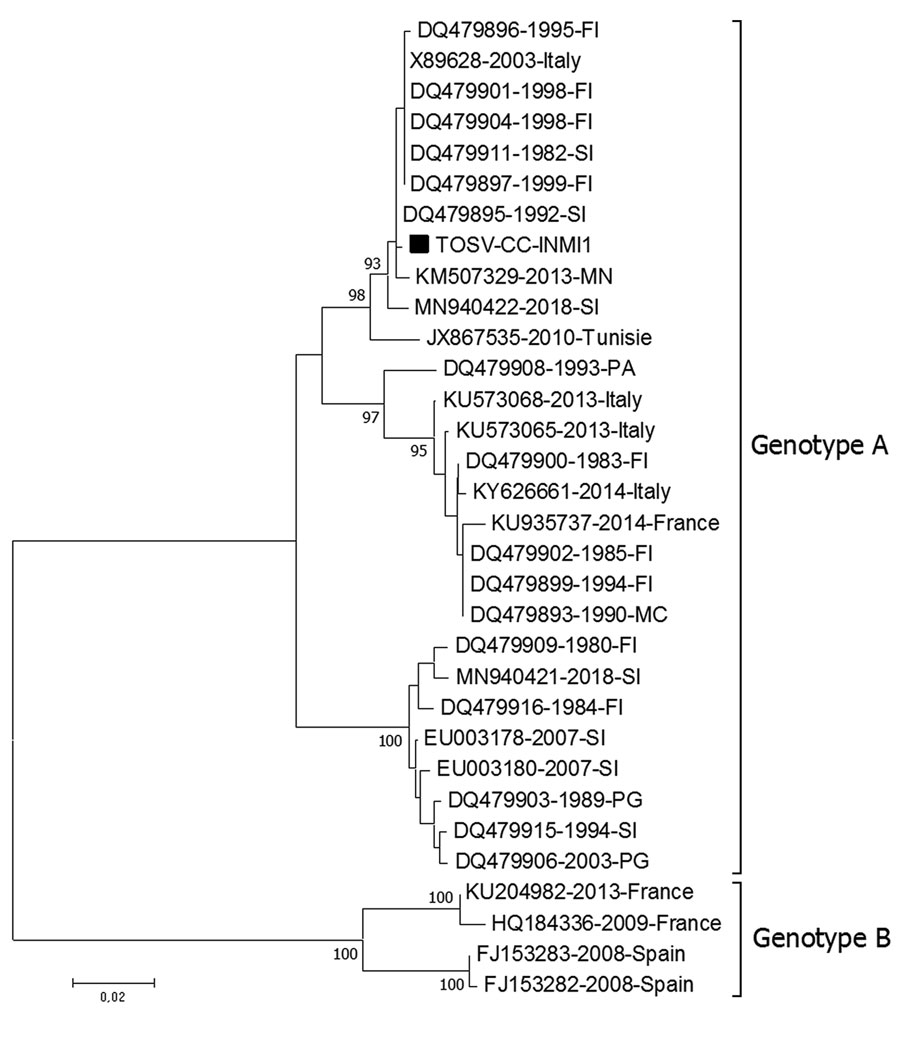
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree based on the partial medium segment of Toscana virus (TOSV) (black square) (nucleotide position 2178–2742 of TOSV reference sequence X89628.1) detected in cerebrospinal fluid of young man returning from Elba Island, Italy. Tree was built using the neighbor-joining method and evolutionary distances computed by using the Kimura 2-parameter method. The rate variation among sites was modeled with a gamma distribution (shape parameter = 0.3). Each record consists of accession number, year, and place of detection/isolation. TOSV genotypes A and B are indicated. Phylogenetic analysis was conducted in the MEGA7 software package (http://www.megasoftware.net). FI, Florence; MC, Macerata; MN, Mantua; PA, Palermo; PG, Perugia; SI, Siena.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: IRCCS Sacro Cuore Don Calabria Hospital, Negrar di Valpolicella, Italy