Volume 28, Number 4—April 2022
Synopsis
Increasing Antimicrobial Resistance in World Health Organization Eastern Mediterranean Region, 2017–2019
Figure 3
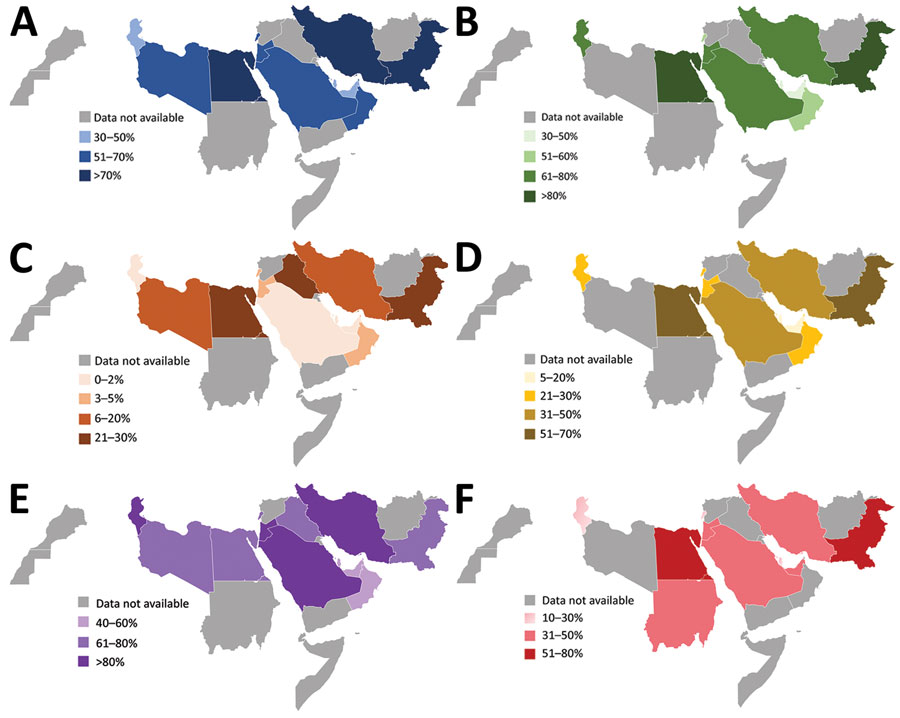
Figure 3. Proportion of patients with bloodstream infections caused by antimicrobial resistant pathogens in World Health Organization Eastern Mediterranean Region countries. Data from the Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (https://www.who.int/glass) for 2019. A) Caused by 3GC-resistant Escherichia coli, 14 countries. B) Caused by K. pneumoniae resistant to 3GC, 12 countries. C) Caused by carbapenem-resistant E. coli, 14 countries. D) Caused by carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, 13 countries. E) Caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp., 12 countries. F) Caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, 12 countries.
Page created: January 10, 2022
Page updated: March 19, 2022
Page reviewed: March 19, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.