Volume 28, Number 5—May 2022
Research Letter
Cross-Variant Neutralizing Serum Activity after SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infections
Figure
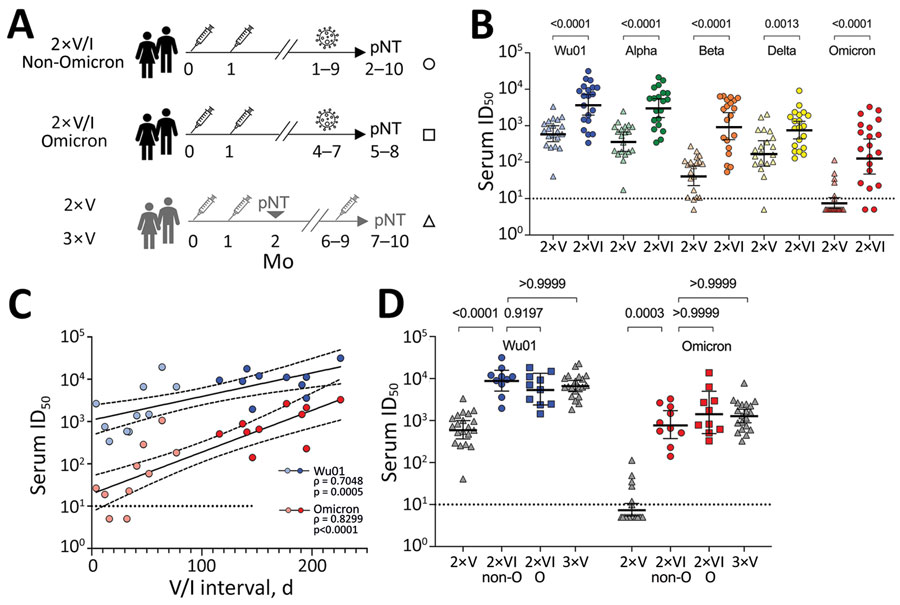
Figure. SARS-CoV-2 serum neutralizing titers across variants after postvaccination breakthrough infection. A) Schematic of the study cohort of 2×VI patients and age-matched reference cohorts (1). B) Serum neutralizing activity against Wu01 and SARS-CoV-2 variants in 2×V persons (triangles) and 2×V/I persons (circles). Horizontal lines indicate geometric mean ID50s; error bars, 95% CIs. Groups were compared by using the Mann-Whitney test. p values are shown at top. C) Correlation of serum neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 Wu01 (blue) or Omicron (red) and interval between second vaccination and non-Omicron breakthrough infection (Spearman ρ and p values). Breakthrough infections within 3 months (90 days) from vaccination are indicated by light shaded symbols. Solid lines indicate linear regression, and dashed lines indicate 95% CIs. Correlation was determined by Spearman ρ. D) Serum neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 Wu01 (blue) and Omicron (red) in 2×V or 3×V persons (triangles) compared with 2×V/I non-Omicron (circles) or Omicron (triangles) persons after 2 and 3 doses of mRNA vaccine. Only persons with vaccine-to-infection intervals >3 months are shown. Groups were compared by using the Kruskal-Wallis test with the Dunn multiple testing correction. Horizontal lines indicate geometric mean ID50s; error bars, 95% CIs. p values are shown at top. Black dotted lines in panels B, C, and D indicate the lower limit of quantification (ID50 = 10); ID50s <10 were imputed to half the lower limit of quantification (ID50 = 5). ID50, 50% inhibitory serum dilution; O, Omicron; pNT, pseudovirus neutralization test; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; V/I, vaccination with subsequent breakthrough infection; Wu01, ancestral (wild-type) SARS-CoV-2 strain; 2xV/I non-Omicron, vaccinated persons with non-Omicron breakthrough infection that occurred 1–8 months after vaccination (circles); 2xV/I Omicron, vaccinated persons with Omicron breakthrough infection that occurred 4–7 months after vaccination (squares); 2xV, vaccinated persons after 2 doses of mRNA vaccine; 3xV, vaccinated persons after 3 doses of mRNA vaccine (triangles).
References
- Gruell H, Vanshylla K, Tober-Lau P, Hillus D, Schommers P, Lehmann C, et al. mRNA booster immunization elicits potent neutralizing serum activity against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Nat Med. 2022; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schmidt F, Muecksch F, Weisblum Y, Da Silva J, Bednarski E, Cho A, et al. Plasma neutralization of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:599–601. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Carreño JM, Alshammary H, Tcheou J, Singh G, Raskin AJ, Kawabata H, et al.; PSP-PARIS Study Group. Activity of convalescent and vaccine serum against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron. Nature. 2022;602:682–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nemet I, Kliker L, Lustig Y, Zuckerman N, Erster O, Cohen C, et al. Third BNT162b2 vaccination neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:492–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bates TA, McBride SK, Winders B, Schoen D, Trautmann L, Curlin ME, et al. Antibody response and variant cross-neutralization after SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection. JAMA. 2022;327:179–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rössler A, Riepler L, Bante D, von Laer D, Kimpel J. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant neutralization in serum from vaccinated and convalescent persons. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:698–700. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2These authors co-led this study.