Volume 28, Number 6—June 2022
Research Letter
Identifying Japanese Encephalitis Virus Using Metatranscriptomic Sequencing, Xinjiang, China
Figure
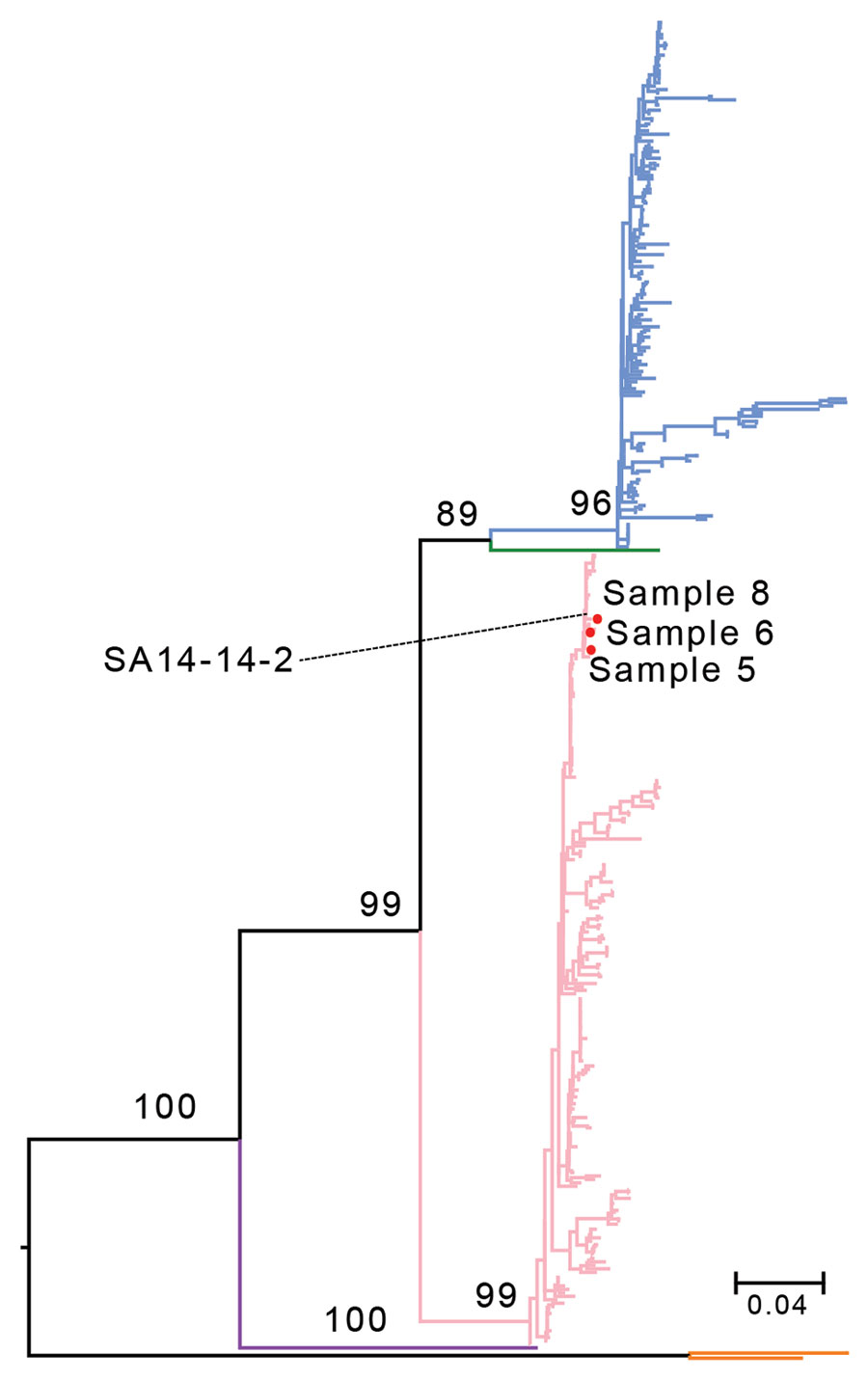
Figure. Maximum-likelihood tree based on the nucleic acid sequences of the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) envelope gene for 3 samples from persons in Xinjiang Province, China (samples 5, 6, and 8), and reference sequences. SA 14-14-2 is the JEV vaccine strain. The branch colors represent different JEV genotypes: blue branches indicate genotype 1; green, genotype 2; pink, genotype 3; purple, genotype 4; and orange, genotype 5. Values at nodes are bootstrap values supporting the branch. Scale bar indicates the substitution rate of equal-length branches.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: March 15, 2022
Page updated: May 22, 2022
Page reviewed: May 22, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.