Volume 28, Number 8—August 2022
Research Letter
Public Health Risk of Foodborne Pathogens in Edible African Land Snails, Cameroon
Figure
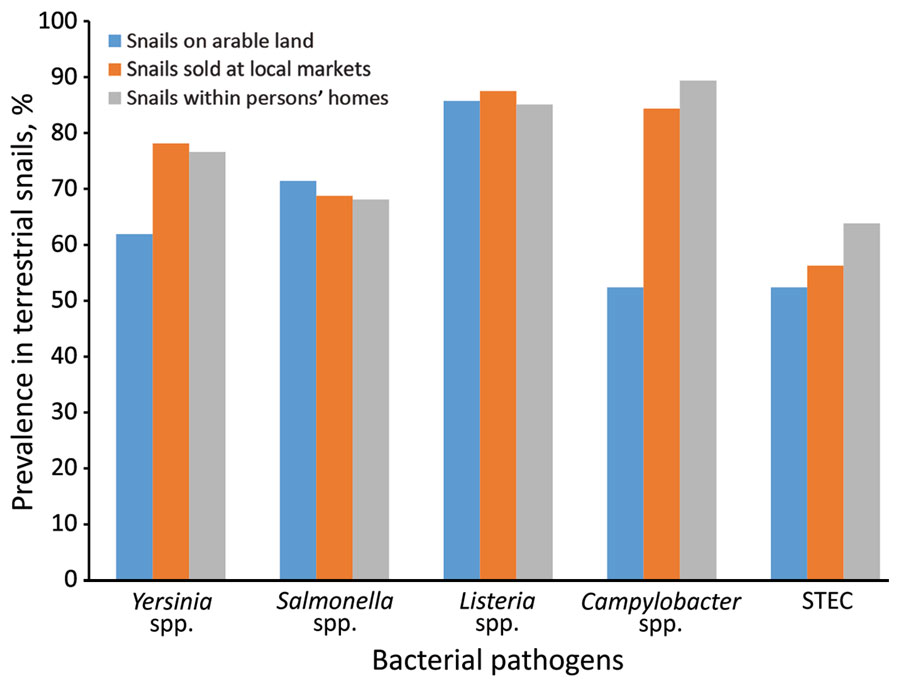
Figure. Prevalence of foodborne pathogens in land snails sampled in 3 selected locations, Buea, Cameroon. June–October 2019. STEC, Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli.
Page created: June 23, 2022
Page updated: July 21, 2022
Page reviewed: July 21, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.