Volume 29, Number 10—October 2023
Policy Review
Managing Risk for Congenital Syphilis, Perth, Western Australia, Australia
Figure 2
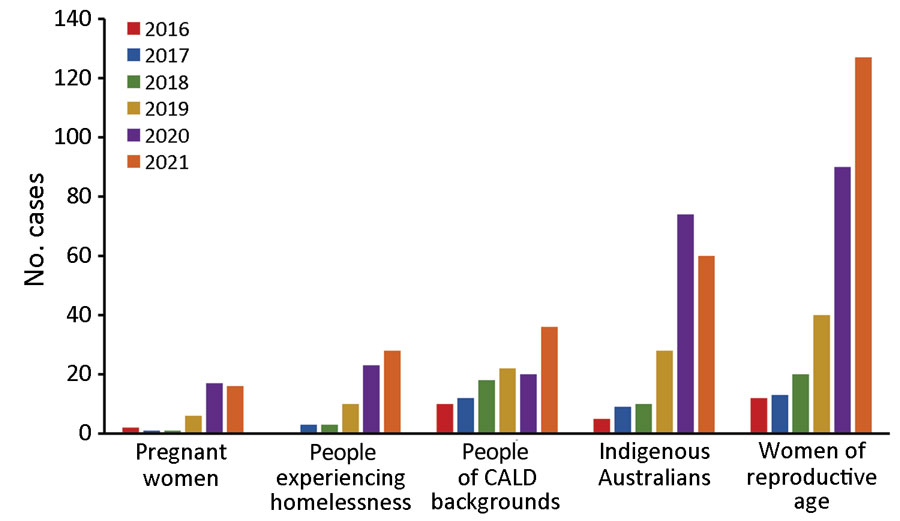
Figure 2. Number of infectious syphilis cases among pregnant women, persons experiencing homelessness, persons of CALD backgrounds, Indigenous Australians, and women of reproductive age, Perth, Western Australia, Australia, 2016–2021. Categories are not mutually exclusive (e.g., a person may fall into >1 category). Data obtained from the Western Australian Notifiable Infectious Diseases Database, Department of Health Western Australia (January 2022) and the Metropolitan Communicable Disease Control Syphilis Register, Metropolitan Communicable Disease Control (January 2022). CALD, culturally and linguistically diverse (persons born in a country other than Australia and who speak a non-English language at home).
Page created: August 03, 2023
Page updated: September 20, 2023
Page reviewed: September 20, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.