Volume 29, Number 11—November 2023
Research
Genotypic Evolution of Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 512 during Ceftazidime/Avibactam, Meropenem/Vaborbactam, and Cefiderocol Treatment, Italy
Figure 2
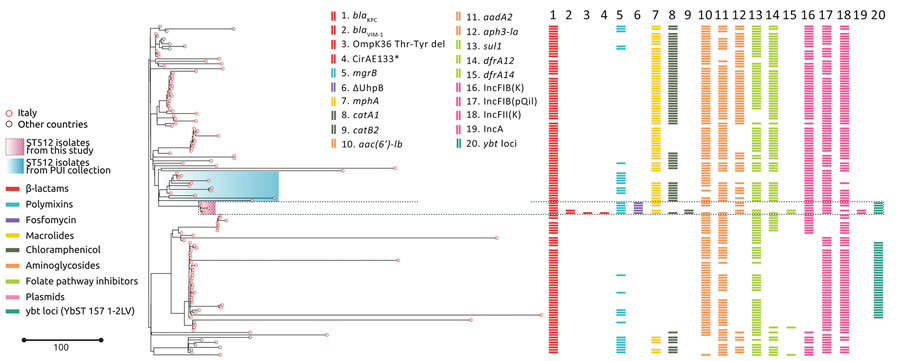
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis and genetic features of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST512 in study of the strain’s genotypic evolution during ceftazidime/avibactam, meropenem/vaborbactam, and cefiderocol treatment, Italy. Phylogenetic tree was constructed from 4,654 core gene alignments from a total of 133 K. pneumoniae ST512 genome sequences: 5 genomes sequenced in this study (pink shading), 12 genomes from the same hospital (pale blue shading), and 116 genomes downloaded from the Pasteur Institute BIGSdb database (https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/klebsiella). Colors indicate resistance and acquired-resistance genes (or corresponding proteins) associated with carbapenemases, yersiniabactin, and chromosomal mutations within the different strains. The same color in the legend on the left indicates the expected resistance phenotype. Asterisk after CirA E133 indicates this mutation produced a premature stop codon. Scale bar indicates number of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the core genome. Del, deletion; KPC, K. pneumoniae carbapenemase; PUI, Policlinico Umberto I; ST, sequence type; VIM, Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase.