Volume 29, Number 12—December 2023
Dispatch
Human Lobomycosis Caused by Paracoccidioides (Lacazia) loboi, Panama, 2022
Figure 2
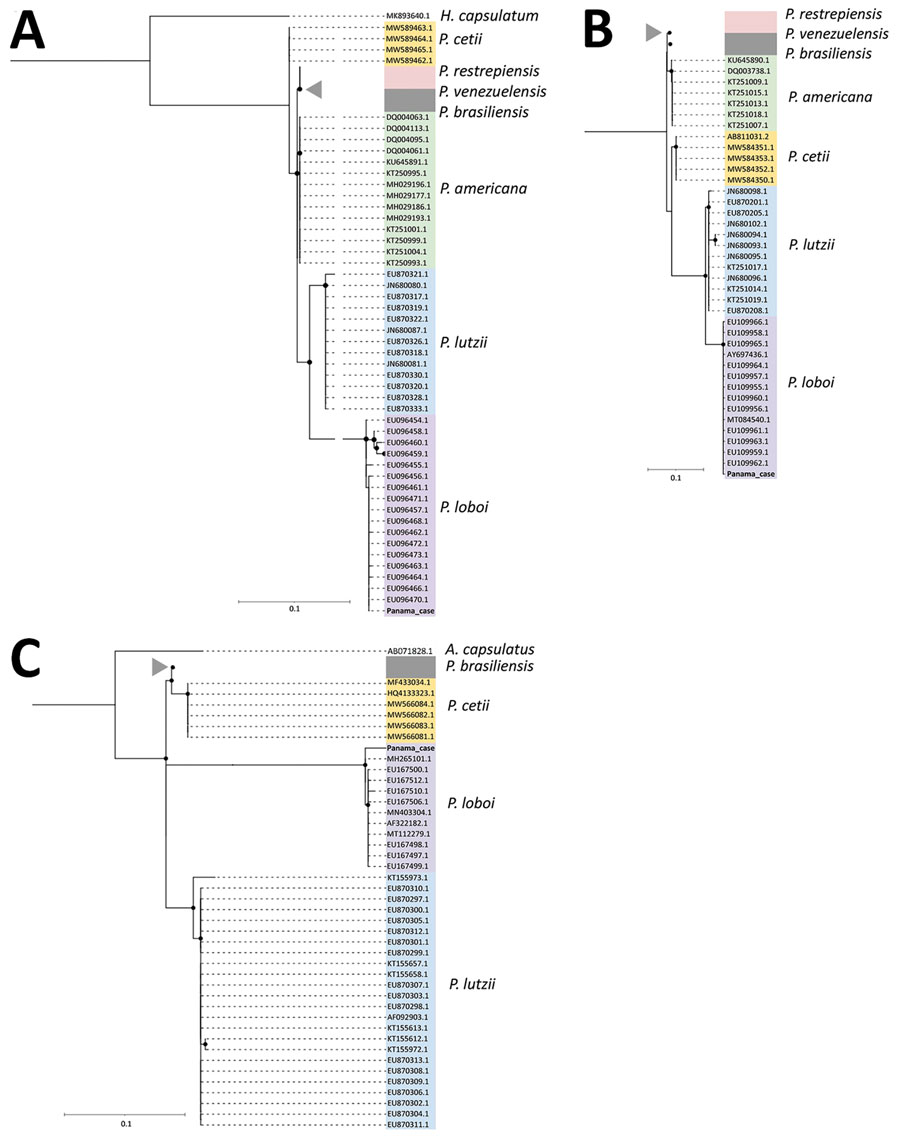
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationship of ADP-rf, Gp43, and internal transcribed spacer (ITS) 1 and 2 genes from patient in Panama who had lobomycosis with other Paracoccidioides species. Trees indicate phylogenetic analysis inferred by maximum-likelihood method of the ADP-rf (A), Gp43 (B), and ITS1–ITS2 (C) genes. Analyses included sequences obtained from research conducted by Vilela et al. (7) and the Panama case analyzed in this study (red). Each color in the trees represent different clusters identified: yellow, Paracoccidioides cetti; white, P. restrepiensis/venezuelensis; gray, P. brasiliensis; green, P. americana; light blue, P. lutzii; and light purple, P. loboi. Gray triangles indicate genomes of the same clade belonging to P. restrepiensis, P. venezuelensis, or P. brasiliensis (to the ADP-rf gene, 49 genomes; to the Gp43 gene, 32 genomes; and to ITS1-ITS2 gene, 52 genomes). Histoplasma capsulatum and Ajellomyces capsulatus DNA sequences were used as outgroups for ADP-rf and ITS genes, respectively. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Paniz-Mondolfi A, Talhari C, Sander Hoffmann L, Connor DL, Talhari S, Bermudez-Villapol L, et al. Lobomycosis: an emerging disease in humans and delphinidae. Mycoses. 2012;55:298–309.
- Lobo JO. New species of blastomycosis [in Portuguese]. Bras Med. 1930;44:1227.
- Vilela R, Huebner M, Vilela C, Vilela G, Pettersen B, Oliveira C, et al. The taxonomy of two uncultivated fungal mammalian pathogens is revealed through phylogeny and population genetic analyses. Sci Rep. 2021;11:18119.
- Lau A, Chen S, Sorrell T, Carter D, Malik R, Martin P, et al. Development and clinical application of a panfungal PCR assay to detect and identify fungal DNA in tissue specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:380–5.
- Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, von Haeseler A, et al. IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol Evol. 2020;37:1530–4.
- Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):
W256–9 . - Vilela R, de Hoog S, Bensch K, Bagagli E, Mendoza L. A taxonomic review of the genus Paracoccidioides, with focus on the uncultivable species. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023;17:
e0011220 . - Herr RA, Tarcha EJ, Taborda PR, Taylor JW, Ajello L, Mendoza L. Phylogenetic analysis of Lacazia loboi places this previously uncharacterized pathogen within the dimorphic Onygenales. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:309–14.
- Bermudez L, Van Bressem MF, Reyes-Jaimes O, Sayegh AJ, Paniz-Mondolfi AE. Lobomycosis in man and lobomycosis-like disease in bottlenose dolphin, Venezuela. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1301–3.
- Taborda PR, Taborda VA, McGinnis MR. Lacazia loboi gen. nov., comb. nov., the etiologic agent of lobomycosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:2031–3.
- Mendoza L, Ajello L, Taylor JW. The taxonomic status of Lacazia loboi and Rhinosporidium seeberi has been finally resolved with the use of molecular tools. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2001;18:95–8.
- Rodrigues AM, Hagen F, Puccia R, Hahn RC, de Camargo ZP. Paracoccidioides and paracoccidioidomycosis in the 21st century. Mycopathologia. 2023;188:129–33.
- Cabañes FJ. Lobomycosis and paracoccidioidomycosis meet again. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2022;39:59–60.
- Francesconi VA, Klein AP, Santos AP, Ramasawmy R, Francesconi F. Lobomycosis: epidemiology, clinical presentation, and management options. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:851–60.
- Tapia A, Torres-Calcindo A, Arosemena R. Keloidal blastomycosis (Lobo’s disease) in Panama. Int J Dermatol. 1978;17:572–4.